Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder[17][7] characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, hearing voices), delusions, disorganized thinking and behavior,[10] and flat or inappropriate affect.[7] Symptoms develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and are never resolved.[3][10] There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person.[10] For a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the described symptoms need to have been present for at least six months (according to the DSM-5) or one month (according to the ICD-11).[10][18] Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially mood, anxiety, and substance use disorders, as well as obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD).[10]
About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime.[19] In 2017, there were an estimated 1.1 million new cases and in 2022 a total of 24 million cases globally.[2][20] Males are more often affected and on average have an earlier onset than females.[2] The causes of schizophrenia may include genetic and environmental factors.[7] Genetic factors include a variety of common and rare genetic variants.[21] Possible environmental factors include being raised in a city, childhood adversity, cannabis use during adolescence, infections, the age of a person's mother or father, and poor nutrition during pregnancy.[7][22]
About half of those diagnosed with schizophrenia will have a significant improvement over the long term with no further relapses, and a small proportion of these will recover completely.[10][23] The other half will have a lifelong impairment.[24] In severe cases, people may be admitted to hospitals.[23] Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty, homelessness, exploitation, and victimization are commonly correlated with schizophrenia.[25][26] Compared to the general population, people with schizophrenia have a higher suicide rate (about 5% overall) and more physical health problems,[27][28] leading to an average decrease in life expectancy by 20[13] to 28 years.[14] In 2015, an estimated 17,000 deaths were linked to schizophrenia.[16]
The mainstay of treatment is antipsychotic medication, including olanzapine and risperidone, along with counseling, job training, and social rehabilitation.[7] Up to a third of people do not respond to initial antipsychotics, in which case clozapine is offered.[29] In a network comparative meta-analysis of 15 antipsychotic drugs, clozapine was significantly more effective than all other drugs, although clozapine's heavily multimodal action may cause more significant side effects.[30] In situations where doctors judge that there is a risk of harm to self or others, they may impose short involuntary hospitalization.[31] Long-term hospitalization is used on a small number of people with severe schizophrenia.[32] In some countries where supportive services are limited or unavailable, long-term hospital stays are more common.[33]
Signs and symptoms

Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by significant alterations in perception, thoughts, mood, and behavior.[34] Symptoms are described in terms of positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms.[3][35] The positive symptoms of schizophrenia are the same for any psychosis and are sometimes referred to as psychotic symptoms. These may be present in any of the different psychoses and are often transient, making early diagnosis of schizophrenia problematic. Psychosis noted for the first time in a person who is later diagnosed with schizophrenia is referred to as a first-episode psychosis (FEP).[36][37]
Positive symptoms
Positive symptoms are those symptoms that are not normally experienced, but are present in people during a psychotic episode in schizophrenia, including delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thoughts, speech and behavior or inappropriate affect, typically regarded as manifestations of psychosis.[36] Hallucinations occur at some point in the lifetimes of 80% of those with schizophrenia[38] and most commonly involve the sense of hearing (most often hearing voices), but can sometimes involve any of the other senses such as taste, sight, smell, and touch.[39] The frequency of hallucinations involving multiple senses is double the rate of those involving only one sense.[38] They are also typically related to the content of the delusional theme.[40] Delusions are bizarre or persecutory in nature. Distortions of self-experience such as feeling that others can hear one's thoughts or that thoughts are being inserted into one's mind, sometimes termed passivity phenomena, are also common.[41][3] Positive symptoms generally respond well to medication[7] and become reduced over the course of the illness, perhaps linked to the age-related decline in dopamine activity.[10]
Negative symptoms
Negative symptoms are deficits of normal emotional responses, or of other thought processes. The five recognized domains of negative symptoms are: blunted affect – showing flat expressions (monotone) or little emotion; alogia – a poverty of speech; anhedonia – an inability to feel pleasure; asociality – the lack of desire to form relationships, and avolition – a lack of motivation and apathy.[42][43] Avolition and anhedonia are seen as motivational deficits resulting from impaired reward processing.[44][45] Reward is the main driver of motivation and this is mostly mediated by dopamine.[45] It has been suggested that negative symptoms are multidimensional and they have been categorised into two subdomains of apathy or lack of motivation, and diminished expression.[42][46] Apathy includes avolition, anhedonia, and social withdrawal; diminished expression includes blunt affect and alogia.[47] Sometimes diminished expression is treated as both verbal and non-verbal.[48]
Apathy accounts for around 50% of the most often found negative symptoms and affects functional outcome and subsequent quality of life. Apathy is related to disrupted cognitive processing affecting memory and planning including goal-directed behaviour.[49] The two subdomains have suggested a need for separate treatment approaches.[50] A lack of distress is another noted negative symptom.[51] A distinction is often made between those negative symptoms that are inherent to schizophrenia, termed primary; and those that result from positive symptoms, from the side effects of antipsychotics, substance use disorder, and social deprivation – termed secondary negative symptoms.[52] Negative symptoms are less responsive to medication and the most difficult to treat.[50] However, if properly assessed, secondary negative symptoms are amenable to treatment.[46] There is some evidence that the negative symptoms of schizophrenia are amenable to psychostimulant medication, although such drugs have varying degrees of risk for causing positive psychotic symptoms.[53]
Scales for specifically assessing the presence of negative symptoms, and for measuring their severity, and their changes have been introduced since the earlier scales such as the PANNS that deals with all types of symptoms.[50] These scales are the Clinical Assessment Interview for Negative Symptoms (CAINS), and the Brief Negative Symptom Scale (BNSS) also known as second-generation scales.[50][51][54] In 2020, ten years after its introduction, a cross-cultural study of the use of BNSS found valid and reliable psychometric evidence for its five-domain structure cross-culturally. The BNSS can assess both the presence and severity of negative symptoms of the five recognized domains and an additional item of reduced normal distress. It has been used to measure changes in negative symptoms in trials of psychosocial and pharmacological interventions.[51]
Cognitive symptoms

An estimated 70% of those with schizophrenia have cognitive deficits, and these are most pronounced in early-onset and late-onset illness.[55][56] These are often evident long before the onset of illness in the prodromal stage, and may be present in childhood or early adolescence.[57][58] They are a core feature but not considered to be core symptoms, as are positive and negative symptoms.[59][60] However, their presence and degree of dysfunction is taken as a better indicator of functionality than the presentation of core symptoms.[57] Cognitive deficits become worse at first episode psychosis but then return to baseline, and remain fairly stable over the course of the illness.[61][62]
The deficits in cognition are seen to drive the negative psychosocial outcome in schizophrenia, and are claimed[by whom?] to equate to a possible reduction in IQ from the norm of 100 to 70–85.[63][64] Cognitive deficits may be of neurocognition (nonsocial) or of social cognition.[55] Neurocognition is the ability to receive and remember information, and includes verbal fluency, memory, reasoning, problem solving, speed of processing, and auditory and visual perception.[62] Verbal memory and attention are seen to be the most affected.[64][65] Verbal memory impairment is associated with a decreased level of semantic processing (relating meaning to words).[66] Another memory impairment is that of episodic memory.[67] An impairment in visual perception that is consistently found in schizophrenia is that of visual backward masking.[62] Visual processing impairments include an inability to perceive complex visual illusions.[68] Social cognition is concerned with the mental operations needed to interpret, and understand the self and others in the social world.[62][55] This is also an associated impairment, and facial emotion perception is often found to be difficult.[69][70] Facial perception is critical for ordinary social interaction.[71] Cognitive impairments do not usually respond to antipsychotics, and there are a number of interventions that are used to try to improve them; cognitive remediation therapy is of particular help.[60]
Neurological soft signs of clumsiness and loss of fine motor movement are often found in schizophrenia, which may resolve with effective treatment of FEP.[18][72]
Onset
Onset typically occurs between the late teens and early 30s, with the peak incidence occurring in males in the early to mid-twenties, and in females in the late twenties.[3][10][18] Onset before the age of 17 is known as early-onset,[73] and before the age of 13, as can sometimes occur, is known as childhood schizophrenia or very early-onset.[10][74] Onset can occur between the ages of 40 and 60, known as late-onset schizophrenia.[55] Onset over the age of 60, which may be difficult to differentiate as schizophrenia, is known as very-late-onset schizophrenia-like psychosis.[55] Late onset has shown that a higher rate of females are affected; they have less severe symptoms and need lower doses of antipsychotics.[55] The tendency for earlier onset in males is later seen to be balanced by a post-menopausal increase in the development in females. Estrogen produced pre-menopause has a dampening effect on dopamine receptors but its protection can be overridden by a genetic overload.[75] There has been a dramatic increase in the numbers of older adults with schizophrenia.[76]
Onset may happen suddenly or may occur after the slow and gradual development of a number of signs and symptoms, a period known as the prodromal stage.[10] Up to 75% of those with schizophrenia go through a prodromal stage.[77] The negative and cognitive symptoms in the prodrome stage can precede FEP (first episode psychosis) by many months and up to five years.[61][78] The period from FEP and treatment is known as the duration of untreated psychosis (DUP) which is seen to be a factor in functional outcome. The prodromal stage is the high-risk stage for the development of psychosis.[62] Since the progression to first episode psychosis is not inevitable, an alternative term is often preferred of at risk mental state.[62] Cognitive dysfunction at an early age impacts a young person's usual cognitive development.[79] Recognition and early intervention at the prodromal stage would minimize the associated disruption to educational and social development and has been the focus of many studies.[61][78]
Risk factors
Schizophrenia is described as a neurodevelopmental disorder with no precise boundary, or single cause, and is thought to develop from gene–environment interactions with involved vulnerability factors.[7][80][81] The interactions of these risk factors are complex, as numerous and diverse insults from conception to adulthood can be involved.[81] A genetic predisposition on its own, without interacting environmental factors, will not give rise to the development of schizophrenia.[81][82] The genetic component means that prenatal brain development is disturbed, and environmental influence affects the postnatal development of the brain.[83] Evidence suggests that genetically susceptible children are more likely to be vulnerable to the effects of environmental risk factors.[83]
Genetic
Estimates of the heritability of schizophrenia are between 70% and 80%, which implies that 70% to 80% of the individual differences in risk of schizophrenia are associated with genetics.[21][84] These estimates vary because of the difficulty in separating genetic and environmental influences, and their accuracy has been queried.[85][86] The greatest risk factor for developing schizophrenia is having a first-degree relative with the disease (risk is 6.5%); more than 40% of identical twins of those with schizophrenia are also affected.[87] If one parent is affected the risk is about 13% and if both are affected the risk is nearly 50%.[84] However, the DSM-5 indicates that most people with schizophrenia have no family history of psychosis.[10] Results of candidate gene studies of schizophrenia have generally failed to find consistent associations,[88] and the genetic loci identified by genome-wide association studies explain only a small fraction of the variation in the disease.[89]
Many genes are known to be involved in schizophrenia, each with small effects and unknown transmission and expression.[21][90][91] The summation of these effect sizes into a polygenic risk score can explain at least 7% of the variability in liability for schizophrenia.[92] Around 5% of cases of schizophrenia are understood to be at least partially attributable to rare copy number variations (CNVs); these structural variations are associated with known genomic disorders involving deletions at 22q11.2 (DiGeorge syndrome) and 17q12 (17q12 microdeletion syndrome), duplications at 16p11.2 (most frequently found) and deletions at 15q11.2 (Burnside–Butler syndrome).[93] Some of these CNVs increase the risk of developing schizophrenia by as much as 20-fold, and are frequently comorbid with autism and intellectual disabilities.[93]
The genes CRHR1 and CRHBP are associated with the severity of suicidal behavior. These genes code for stress response proteins needed in the control of the HPA axis, and their interaction can affect this axis. Response to stress can cause lasting changes in the function of the HPA axis possibly disrupting the negative feedback mechanism, homeostasis, and the regulation of emotion leading to altered behaviors.[82]
The question of how schizophrenia could be primarily genetically influenced, given that people with schizophrenia have lower fertility rates, is a paradox. It is expected that genetic variants that increase the risk of schizophrenia would be selected against, due to their negative effects on reproductive fitness. A number of potential explanations have been proposed, including that alleles associated with schizophrenia risk confers a fitness advantage in unaffected individuals.[94][95] While some evidence has not supported this idea,[86] others propose that a large number of alleles each contributing a small amount can persist.[96]
A meta-analysis found that oxidative DNA damage was significantly increased in schizophrenia.[97]
Environmental
Environmental factors, each associated with a slight risk of developing schizophrenia in later life include oxygen deprivation, infection, prenatal maternal stress, and malnutrition in the mother during prenatal development.[98] A risk is associated with maternal obesity, in increasing oxidative stress, and dysregulating the dopamine and serotonin pathways.[99] Both maternal stress and infection have been demonstrated to alter fetal neurodevelopment through an increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines.[100] There is a slighter risk associated with being born in the winter or spring possibly due to vitamin D deficiency[101] or a prenatal viral infection.[87] Other infections during pregnancy or around the time of birth that have been linked to an increased risk include infections by Toxoplasma gondii and Chlamydia.[102] The increased risk is about five to eight percent.[103] Viral infections of the brain during childhood are also linked to a risk of schizophrenia during adulthood.[104] Cat exposure is also associated with an increased risk of broadly defined schizophrenia-related disorders, with an odds ratio of 2.4.[105]
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), severe forms of which are classed as childhood trauma, range from being bullied or abused, to the death of a parent.[106] Many adverse childhood experiences can cause toxic stress and increase the risk of psychosis.[106][107][108] Chronic trauma, including ACEs, can promote lasting inflammatory dysregulation throughout the nervous system.[109] It is suggested that early stress may contribute to the development of schizophrenia through these alterations in the immune system.[109] Schizophrenia was the last diagnosis to benefit from the link made between ACEs and adult mental health outcomes.[110]
Living in an urban environment during childhood or as an adult has consistently been found to increase the risk of schizophrenia by a factor of two,[27][111] even after taking into account drug use, ethnic group, and size of social group.[112] A possible link between the urban environment and pollution has been suggested to be the cause of the elevated risk of schizophrenia.[113] Other risk factors include social isolation, immigration related to social adversity and racial discrimination, family dysfunction, unemployment, and poor housing conditions.[87][114] Having a father older than 40 years, or parents younger than 20 years are also associated with schizophrenia.[7][115]
Substance use
About half of those with schizophrenia use recreational drugs including alcohol, tobacco, and cannabis excessively.[116][117] Use of stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine can lead to a temporary stimulant psychosis, which presents very similarly to schizophrenia. Rarely, alcohol use can also result in a similar alcohol-related psychosis.[87][118] Drugs may also be used as coping mechanisms by people who have schizophrenia, to deal with depression, anxiety, boredom, and loneliness.[116][119] The use of cannabis and tobacco are not associated with the development of cognitive deficits, and sometimes a reverse relationship is found where their use improves these symptoms.[60] However, substance use disorders are associated with an increased risk of suicide, and a poor response to treatment.[120][121]
Cannabis use may be a contributory factor in the development of schizophrenia, potentially increasing the risk of the disease in those who are already at risk.[122][123][124] The increased risk may require the presence of certain genes within an individual.[22] Its use is associated with doubling the rate.[125]
Causes
The causes of schizophrenia are still unknown. Several models have been put forward to explain the link between altered brain function and schizophrenia.[27] The prevailing model of schizophrenia is that of a neurodevelopmental disorder, and the underlying changes that occur before symptoms become evident are seen as arising from the interaction between genes and the environment.[126] Extensive studies support this model.[77] Maternal infections, malnutrition and complications during pregnancy and childbirth are known risk factors for the development of schizophrenia, which usually emerges between the ages of 18 and 25, a period that overlaps with certain stages of neurodevelopment.[127] Gene-environment interactions lead to deficits in the neural circuitry that affect sensory and cognitive functions.[77]
The common dopamine and glutamate models proposed are not mutually exclusive; each is seen to have a role in the neurobiology of schizophrenia.[128] The most common model put forward was the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia, which attributes psychosis to the mind's faulty interpretation of the misfiring of dopaminergic neurons.[129] This has been directly related to the symptoms of delusions and hallucinations.[130][131][132] Abnormal dopamine signaling has been implicated in schizophrenia based on the usefulness of medications that affect the dopamine receptor and the observation that dopamine levels are increased during acute psychosis.[133][134] A decrease in D1 receptors in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex may also be responsible for deficits in working memory.[135][136]
The glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia links alterations between glutamatergic neurotransmission and the neural oscillations that affect connections between the thalamus and the cortex.[137] Studies have shown that a reduced expression of a glutamate receptor – NMDA receptor, and glutamate blocking drugs such as phencyclidine and ketamine can mimic the symptoms and cognitive problems associated with schizophrenia.[137][138][139] Post-mortem studies consistently find that a subset of these neurons fail to express GAD67 (GAD1),[140] in addition to abnormalities in brain morphometry. The subsets of interneurons that are abnormal in schizophrenia are responsible for the synchronizing of neural ensembles needed during working memory tasks. These give the neural oscillations produced as gamma waves that have a frequency of between 30 and 80 hertz. Both working memory tasks and gamma waves are impaired in schizophrenia, which may reflect abnormal interneuron functionality.[140][141][142][143] An important process that may be disrupted in neurodevelopment is astrogenesis – the formation of astrocytes. Astrocytes are crucial in contributing to the formation and maintenance of neural circuits and it is believed that disruption in this role can result in a number of neurodevelopmental disorders including schizophrenia.[144] Evidence suggests that reduced numbers of astrocytes in deeper cortical layers are assocociated with a diminished expression of EAAT2, a glutamate transporter in astrocytes; supporting the glutamate hypothesis.[144]
Deficits in executive functions, such as planning, inhibition, and working memory, are pervasive in schizophrenia. Although these functions are separable, their dysfunction in schizophrenia may reflect an underlying deficit in the ability to represent goal related information in working memory, and to use this to direct cognition and behavior.[145][146] These impairments have been linked to a number of neuroimaging and neuropathological abnormalities. For example, functional neuroimaging studies report evidence of reduced neural processing efficiency, whereby the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is activated to a greater degree to achieve a certain level of performance relative to controls on working memory tasks. These abnormalities may be linked to the consistent post-mortem finding of reduced neuropil, evidenced by increased pyramidal cell density and reduced dendritic spine density. These cellular and functional abnormalities may also be reflected in structural neuroimaging studies that find reduced grey matter volume in association with deficits in working memory tasks.[147]
Positive symptoms have been linked to cortical thinning in the superior temporal gyrus.[148] The severity of negative symptoms has been linked to reduced thickness in the left medial orbitofrontal cortex.[149] Anhedonia, traditionally defined as a reduced capacity to experience pleasure, is frequently reported in schizophrenia. However, a large body of evidence suggests that hedonic responses are intact in schizophrenia,[150] and that what is reported to be anhedonia is a reflection of dysfunction in other processes related to reward.[151] Overall, a failure of reward prediction is thought to lead to impairment in the generation of cognition and behavior required to obtain rewards, despite normal hedonic responses.[152]
Another theory links abnormal brain lateralization to the development of being left-handed which is significantly more common in those with schizophrenia.[153] This abnormal development of hemispheric asymmetry is noted in schizophrenia.[154] Studies have concluded that the link is a true and verifiable effect that may reflect a genetic link between lateralization and schizophrenia.[153][155]
Bayesian models of brain functioning have been used to link abnormalities in cellular functioning to symptoms.[156][157] Both hallucinations and delusions have been suggested to reflect improper encoding of prior expectations, thereby causing expectation to excessively influence sensory perception and the formation of beliefs. In approved models of circuits that mediate predictive coding, reduced NMDA receptor activation, could in theory result in the positive symptoms of delusions and hallucinations.[158][159][160]
Diagnosis
Criteria
Schizophrenia is diagnosed based on criteria in either the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) published by the American Psychiatric Association or the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) published by the World Health Organization (WHO). These criteria use the self-reported experiences of the person and reported abnormalities in behavior, followed by a psychiatric assessment. The mental status examination is an important part of the assessment.[161] An established tool for assessing the severity of positive and negative symptoms is the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS).[162] This has been seen to have shortcomings relating to negative symptoms, and other scales – the Clinical Assessment Interview for Negative Symptoms (CAINS), and the Brief Negative Symptoms Scale (BNSS) have been introduced.[50] The DSM-5, published in 2013, gives a Scale to Assess the Severity of Symptom Dimensions outlining eight dimensions of symptoms.[59]
DSM-5 states that to be diagnosed with schizophrenia, two diagnostic criteria have to be met over the period of one month, with a significant impact on social or occupational functioning for at least six months. One of the symptoms needs to be either delusions, hallucinations, or disorganized speech. A second symptom could be one of the negative symptoms, or severely disorganized or catatonic behaviour.[10] A different diagnosis of schizophreniform disorder can be made before the six months needed for the diagnosis of schizophrenia.[10]
In Australia, the guideline for diagnosis is for six months or more with symptoms severe enough to affect ordinary functioning.[163] In the UK diagnosis is based on having the symptoms for most of the time for one month, with symptoms that significantly affect the ability to work, study, or carry on ordinary daily living, and with other similar conditions ruled out.[164]
The ICD criteria are typically used in European countries; the DSM criteria are used predominantly in the United States and Canada, and are prevailing in research studies. In practice, agreement between the two systems is high.[165] The current proposal for the ICD-11 criteria for schizophrenia recommends adding self-disorder as a symptom.[41]
A major unresolved difference between the two diagnostic systems is that of the requirement in DSM of an impaired functional outcome. WHO for ICD argues that not all people with schizophrenia have functional deficits and so these are not specific for the diagnosis.[59]
Neuroimaging techniques
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has become a tool in understanding brain activity and connectivity differences in individuals with schizophrenia. Through resting-state fMRI, researchers have observed altered connectivity patterns within several key brain networks, such as the default mode network (DMN),[166] salience network (SN),[167] and central executive network (CEN).[168] Alterations may underlie cognitive and emotional symptoms in schizophrenia, such as disorganized thinking, impaired attention, and emotional dysregulation.
Comorbidities

Many people with schizophrenia may have one or more other mental disorders, such as anxiety disorders, obsessive–compulsive disorder, or substance use disorder. These are separate disorders that require treatment.[10] When comorbid with schizophrenia, substance use disorder and antisocial personality disorder both increase the risk for violence.[169] Comorbid substance use disorder also increases the risk of suicide.[120]
Sleep disorders often co-occur with schizophrenia, and may be an early sign of relapse.[170] Sleep disorders are linked with positive symptoms such as disorganized thinking and can adversely affect cortical plasticity and cognition.[170] The consolidation of memories is disrupted in sleep disorders.[171] They are associated with severity of illness, a poor prognosis, and poor quality of life.[172][173] Sleep onset and maintenance insomnia is a common symptom, regardless of whether treatment has been received or not.[172] Genetic variations have been found associated with these conditions involving the circadian rhythm, dopamine and histamine metabolism, and signal transduction.[174]
Schizophrenia is also associated with a number of somatic comorbidities including diabetes mellitus type 2, autoimmune diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. The association of these with schizophrenia may be partially due to medications (e.g. dyslipidemia from antipsychotics), environmental factors (e.g. complications from an increased rate of cigarette smoking), or associated with the disorder itself (e.g. diabetes mellitus type 2 and some cardiovascular diseases are thought to be genetically linked). These somatic comorbidities contribute to reduced life expectancy among persons with the disorder.[175]
Differential diagnosis
To make a diagnosis of schizophrenia other possible causes of psychosis need to be excluded.[176]: 858 Psychotic symptoms lasting less than a month may be diagnosed as brief psychotic disorder, or as schizophreniform disorder. Psychosis is noted in Other specified schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders as a DSM-5 category. Schizoaffective disorder is diagnosed if symptoms of mood disorder are substantially present alongside psychotic symptoms. Psychosis that results from a general medical condition or substance is termed secondary psychosis.[10]
Psychotic symptoms may be present in several other conditions, including bipolar disorder,[11] borderline personality disorder,[12] substance intoxication, substance-induced psychosis, and a number of drug withdrawal syndromes. Non-bizarre delusions are also present in delusional disorder, and social withdrawal in social anxiety disorder, avoidant personality disorder and schizotypal personality disorder. Schizotypal personality disorder has symptoms that are similar but less severe than those of schizophrenia.[10] Schizophrenia occurs along with obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) considerably more often than could be explained by chance, although it can be difficult to distinguish obsessions that occur in OCD from the delusions of schizophrenia.[177] There can be considerable overlap with the symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder.[178]
A more general medical and neurological examination may be needed to rule out medical illnesses which may rarely produce psychotic schizophrenia-like symptoms, such as metabolic disturbance, systemic infection, syphilis, HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder, epilepsy, limbic encephalitis, and brain lesions. Stroke, multiple sclerosis, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and dementias such as Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, frontotemporal dementia, and the Lewy body dementias may also be associated with schizophrenia-like psychotic symptoms.[179] It may be necessary to rule out a delirium, which can be distinguished by visual hallucinations, acute onset and fluctuating level of consciousness, and indicates an underlying medical illness. Investigations are not generally repeated for relapse unless there is a specific medical indication or possible adverse effects from antipsychotic medication.[180] In children hallucinations must be separated from typical childhood fantasies.[10] It is difficult to distinguish childhood schizophrenia from autism.[74]
Prevention
Prevention of schizophrenia is difficult as there are no reliable markers for the later development of the disorder.[181]
Early intervention programs diagnose and treat patients in the prodromal phase of the illness. There is some evidence that these programs reduce symptoms. Patients tend to prefer early treatment programs to ordinary treatment and are less likely to disengage from them. As of 2020, it is unclear whether the benefits of early treatment persist once the treatment is terminated.[182]
Cognitive behavioral therapy may reduce the risk of psychosis in those at high risk after a year[183] and is recommended in this group, by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE).[34] Another preventive measure is to avoid drugs that have been associated with development of the disorder, including cannabis, cocaine, and amphetamines.[87]
Antipsychotics are prescribed following a first-episode psychosis, and following remission, a preventive maintenance use is continued to avoid relapse. However, it is recognized that some people do recover following a single episode and that long-term use of antipsychotics will not be needed but there is no way of identifying this group.[184]
Management
The primary treatment of schizophrenia is the use of antipsychotic medications, often in combination with psychosocial interventions and social supports.[27][185] Community support services including drop-in centers, visits by members of a community mental health team, supported employment,[186] and support groups are common. The time between the onset of psychotic symptoms to being given treatment – the duration of untreated psychosis (DUP) – is associated with a poorer outcome in both the short term and the long term.[187]
Voluntary or involuntary admission to hospital may be imposed by doctors and courts who deem a person to be having a severe episode. In the UK, large mental hospitals termed asylums began to be closed down in the 1950s with the advent of antipsychotics, and with an awareness of the negative impact of long-term hospital stays on recovery.[25] This process was known as deinstitutionalization, and community and supportive services were developed to support this change. Many other countries followed suit with the US starting in the 60s.[188] There still remain a smaller group of people who do not improve enough to be discharged.[25][32] In some countries that lack the necessary supportive and social services, long-term hospital stays are more usual.[33]
Medication

The first-line treatment for schizophrenia is an antipsychotic. The first-generation antipsychotics, now called typical antipsychotics, like haloperidol, are dopamine antagonists that block D2 receptors, and affect the neurotransmission of dopamine. Those brought out later, the second-generation antipsychotics known as atypical antipsychotics, including olanzapine and risperidone, can also have an effect on another neurotransmitter, serotonin. Antipsychotics can reduce the symptoms of anxiety within hours of their use, but, for other symptoms, they may take several days or weeks to reach their full effect.[36][189] They have little effect on negative and cognitive symptoms, which may be helped by additional psychotherapies and medications.[190] There is no single antipsychotic suitable for first-line treatment for everyone, as responses and tolerances vary between people.[191] Stopping medication may be considered after a single psychotic episode where there has been a full recovery with no symptoms for twelve months. Repeated relapses worsen the long-term outlook and the risk of relapse following a second episode is high, and long-term treatment is usually recommended.[192][193]
About half of those with schizophrenia will respond favourably to antipsychotics, and have a good return of functioning.[194] However, positive symptoms persist in up to a third of people. Following two trials of different antipsychotics over six weeks, that also prove ineffective, they will be classed as having treatment-resistant schizophrenia (TRS), and clozapine will be offered.[195][29] Clozapine is of benefit to around half of this group although it has the potentially serious side effect of agranulocytosis (lowered white blood cell count) in less than 4% of people.[27][87][196]
About 30 to 50 percent of people with schizophrenia do not accept that they have an illness or comply with their recommended treatment.[197] For those who are unwilling or unable to take medication regularly, long-acting injections of antipsychotics may be used,[198] which reduce the risk of relapse to a greater degree than oral medications.[199] When used in combination with psychosocial interventions, they may improve long-term adherence to treatment.[200]
The fixed-dose combination medication xanomeline/trospium chloride (Cobenfy) was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2024.[201][202] It is the first cholinergic agonist approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat schizophrenia.[201]
Negative and cognitive symptoms are an unmet clinical need in antipsychotic-based treatment approaches. Psychostimulant drugs have been found effective in the treatment of negative symptoms, but are rarely prescribed due to concerns about the excacerbation of positive symptoms.[203] It is possible that low-dose psychedelic therapies could be of benefit in schizophrenia through their prosocial and procognitive effects, although there is a serious risk that high dose psychedelic therapies could lead to worsening of positive symptoms.[204]
Adverse effects
Extrapyramidal symptoms, including akathisia, are associated with all commercially available antipsychotic to varying degrees.[205]: 566 There is little evidence that second generation antipsychotics have reduced levels of extrapyramidical symptoms compared to typical antipsychotics.[205]: 566 Tardive dyskinesia can occur due to long-term use of antipsychotics, developing after months or years of use.[206] The antipsychotic clozapine is also associated with thromboembolism (including pulmonary embolism), myocarditis, and cardiomyopathy.
Psychosocial interventions
A number of psychosocial interventions that include several types of psychotherapy may be useful in the treatment of schizophrenia such as: family therapy,[207] group therapy, cognitive remediation therapy (CRT),[208] cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and metacognitive training.[209][210] Skills training, help with substance use, and weight management – often needed as a side effect of an antipsychotic – are also offered.[211] In the US, interventions for first episode psychosis have been brought together in an overall approach known as coordinated speciality care (CSC) and also includes support for education.[36] In the UK care across all phases is a similar approach that covers many of the treatment guidelines recommended.[34] The aim is to reduce the number of relapses and stays in the hospital.[207]
Other support services for education, employment, and housing are usually offered. For people with severe schizophrenia, who are discharged from a stay in the hospital, these services are often brought together in an integrated approach to offer support in the community away from the hospital setting. In addition to medicine management, housing, and finances, assistance is given for more routine matters such as help with shopping and using public transport. This approach is known as assertive community treatment (ACT) and has been shown to achieve positive results in symptoms, social functioning and quality of life.[212][213] Another more intense approach is known as intensive care management (ICM). ICM is a stage further than ACT and emphasises support of high intensity in smaller caseloads, (less than twenty). This approach is to provide long-term care in the community. Studies show that ICM improves many of the relevant outcomes including social functioning.[214]
Some studies have shown little evidence for the effectiveness of CBT in either reducing symptoms or preventing relapse.[215][216] However, other studies have found that CBT does improve overall psychotic symptoms (when in use with medication) and it has been recommended in Canada, but has been seen to have no effect on social function, relapse, or quality of life.[217] In the UK it is recommended as an add-on therapy in the treatment of schizophrenia.[189][216] Arts therapies are seen to improve negative symptoms in some people, and are recommended by NICE in the UK.[189] This approach is criticised as having not been well-researched,[218][219] and arts therapies are not recommended in Australian guidelines for example.[220] Peer support, in which people with personal experience of schizophrenia, provide help to each other, is of unclear benefit.[221]
Other
Exercise including aerobic exercise has been shown to improve positive and negative symptoms, cognition, working memory, and improve quality of life.[222][223] Exercise has also been shown to increase the volume of the hippocampus in those with schizophrenia. A decrease in hippocampal volume is one of the factors linked to the development of the disease.[222] However, there still remains the problem of increasing motivation for, and maintaining participation in physical activity.[224] Supervised sessions are recommended.[223] In the UK healthy eating advice is offered alongside exercise programs.[225]
An inadequate diet is often found in schizophrenia, and associated vitamin deficiencies including those of folate, and vitamin D are linked to the risk factors for the development of schizophrenia and for early death including heart disease.[226][227] Those with schizophrenia possibly have the worst diet of all the mental disorders. Lower levels of folate and vitamin D have been noted as significantly lower in first episode psychosis.[226] The use of supplemental folate is recommended.[228] A zinc deficiency has also been noted.[229] Vitamin B12 is also often deficient and this is linked to worse symptoms. Supplementation with B vitamins has been shown to significantly improve symptoms, and to put in reverse some of the cognitive deficits.[226] It is also suggested that the noted dysfunction in gut microbiota might benefit from the use of probiotics.[229]
Prognosis

| no data ≤ 185 185–197 197–207 207–218 218–229 229–240 | 240–251 251–262 262–273 273–284 284–295 ≥ 295 |
Schizophrenia has great human and economic costs.[7] It decreases life expectancy by between 10[13] and 28 years.[14] This is primarily because of its association with heart disease,[230] diabetes,[14] obesity, poor diet, a sedentary lifestyle, and smoking, with an increased rate of suicide playing a lesser role.[13][231] Side effects of antipsychotics may also increase the risk.[13]
Almost 40% of those with schizophrenia die from complications of cardiovascular disease which is seen to be increasingly associated.[227] An underlying factor of sudden cardiac death may be Brugada syndrome (BrS) – BrS mutations that overlap with those linked with schizophrenia are the calcium channel mutations.[227] BrS may also be drug-induced from certain antipsychotics and antidepressants.[227] Primary polydipsia, or excessive fluid intake, is relatively common in people with chronic schizophrenia.[232][233] This may lead to hyponatremia which can be life-threatening. Antipsychotics can lead to a dry mouth, but there are several other factors that may contribute to the disorder; it may reduce life expectancy by 13 percent.[233] Barriers to improving the mortality rate in schizophrenia are poverty, overlooking the symptoms of other illnesses, stress, stigma, and medication side effects.[234]
Schizophrenia is a major cause of disability. In 2016, it was classed as the 12th most disabling condition.[235] Approximately 75% of people with schizophrenia have ongoing disability with relapses.[236] Some people do recover completely and others function well in society.[237] Most people with schizophrenia live independently with community support.[27] About 85% are unemployed.[7] In people with a first episode of psychosis in schizophrenia a good long-term outcome occurs in 31%, an intermediate outcome in 42% and a poor outcome in 31%.[238] Males are affected more often than females, and have a worse outcome.[239] Studies showing that outcomes for schizophrenia appear better in the developing than the developed world[240] have been questioned.[241] Social problems, such as long-term unemployment, poverty, homelessness, exploitation, stigmatization and victimization are common consequences, and lead to social exclusion.[25][26]
There is a higher than average suicide rate associated with schizophrenia estimated at 5% to 6%, most often occurring in the period following onset or first hospital admission.[18][28] Several times more (20 to 40%) attempt suicide at least once.[10][101] There are a variety of risk factors, including male sex, depression, a high IQ,[242] heavy smoking,[243] and substance use.[120] Repeated relapse is linked to an increased risk of suicidal behavior.[184] The use of clozapine can reduce the risk of suicide, and of aggression.[244]
A strong association between schizophrenia and tobacco smoking has been shown in worldwide studies.[245][246] Smoking is especially high in those diagnosed with schizophrenia, with estimates ranging from 80 to 90% being regular smokers, as compared to 20% of the general population.[246] Those who smoke tend to smoke heavily, and additionally smoke cigarettes with high nicotine content.[40] Some propose that this is in an effort to improve symptoms.[247] Among people with schizophrenia use of cannabis is also common.[120]
Schizophrenia leads to an increased risk of dementia.[248]
Violence
Most people with schizophrenia are not aggressive, and are more likely to be victims of violence rather than perpetrators.[10] People with schizophrenia are commonly exploited and victimized by violent crime as part of a broader dynamic of social exclusion.[25][26] People diagnosed with schizophrenia are also subject to forced drug injections, seclusion, and restraint at high rates.[31][32]
The risk of violence by people with schizophrenia is small. There are minor subgroups where the risk is high.[169] This risk is usually associated with a comorbid disorder such as a substance use disorder – in particular alcohol, or with antisocial personality disorder.[169] Substance use disorder is strongly linked, and other risk factors are linked to deficits in cognition and social cognition including facial perception and insight that are in part included in theory of mind impairments.[249][250] Poor cognitive functioning, decision-making, and facial perception may contribute to making a wrong judgement of a situation that could result in an inappropriate response such as violence.[251] These associated risk factors are also present in antisocial personality disorder which when present as a comorbid disorder greatly increases the risk of violence.[252][253]
Epidemiology
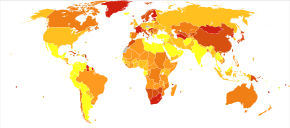
In 2017,[needs update] the Global Burden of Disease Study estimated there were 1.1 million new cases;[20] in 2022 the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a total of 24 million cases globally.[2] Schizophrenia affects around 0.3–0.7% of people at some point in their life.[19][14] In areas of conflict this figure can rise to between 4.0 and 6.5%.[254] It occurs 1.4 times more frequently in males than females and typically appears earlier in men.[87]
Worldwide, schizophrenia is the most common psychotic disorder.[56] The frequency of schizophrenia varies across the world,[10] within countries,[255] and at the local and neighborhood level;[256] this variation in prevalence between studies over time, across geographical locations, and by gender is as high as fivefold.[7]
Schizophrenia causes approximately one percent of worldwide disability adjusted life years[needs update][87] and resulted in 17,000 deaths in 2015.[16]
In 2000,[needs update] WHO found the percentage of people affected and the number of new cases that develop each year is roughly similar around the world, with age-standardized prevalence per 100,000 ranging from 343 in Africa to 544 in Japan and Oceania for men, and from 378 in Africa to 527 in Southeastern Europe for women.[257]
History
Conceptual development

Accounts of a schizophrenia-like syndrome are rare in records before the 19th century; the earliest case reports were in 1797 and 1809.[258] The term dementia praecox ("premature dementia") was used by German psychiatrist Heinrich Schüle in 1886 and then in 1891 by Arnold Pick in a case report of hebephrenia. In 1893 Emil Kraepelin used the term in making a distinction, known as the Kraepelinian dichotomy, between the two psychoses: dementia praecox and manic depression (now called bipolar disorder).[13] When it became evident that the disorder was not a degenerative dementia, it was renamed schizophrenia by Eugen Bleuler in 1908.[259]
The word schizophrenia ("splitting of the mind") is Modern Latin, derived from the Greek schizein (Ancient Greek: σχίζειν, lit. 'to split') and phrēn (Ancient Greek: φρήν, lit. 'mind').[260] Its use was intended to describe the separation of function between personality, thinking, memory, and perception.[259]
In the early 20th century, the psychiatrist Kurt Schneider categorized the psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia into two groups: hallucinations and delusions. The hallucinations were listed as specific to auditory and the delusions included thought disorders. These were seen as important symptoms, termed first-rank. The most common first-rank symptom was found to belong to thought disorders.[page needed][261][page needed][262] In 2013 the first-rank symptoms were excluded from the DSM-5 criteria;[263] while they may not be useful in diagnosing schizophrenia, they can assist in differential diagnosis.[264]
Subtypes of schizophrenia—classified as paranoid, disorganized, catatonic, undifferentiated, and residual—were difficult to distinguish and are no longer recognized as separate conditions by DSM-5 (2013) or ICD-11.[265][266][267]
Breadth of diagnosis
Before the 1960s, nonviolent petty criminals and women were sometimes diagnosed with schizophrenia, categorizing the latter as ill for not performing their duties as wives and mothers.[268] In the mid- to late 1960s, black men were categorized as "hostile and aggressive" and diagnosed as schizophrenic at much higher rates, their civil rights and Black Power activism labeled as delusions.[268][269]
In the early 1970s in the United States, the diagnostic model for schizophrenia was broad and clinically based using DSM II. Schizophrenia was diagnosed far more in the United States than in Europe, where the ICD-9 criteria were followed. The US model was criticised for failing to demarcate clearly those people with a mental illness. In 1980 DSM III was published and showed a shift in focus from the clinically based biopsychosocial model to a reason-based medical model.[clarification needed][270] DSM IV brought an increased focus on an evidence-based medical model.[271]
Historical treatment

In the 1930s a number of shock procedures which induced seizures (convulsions) or comas were used to treat schizophrenia.[272] Insulin shock involved injecting large doses of insulin to induce comas, which in turn produced hypoglycemia and convulsions.[272][273] The use of electricity to induce seizures was in use as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) by 1938.[274]
Carried out from the 1930s until the 1970s in the United States and until the 1980s in France, psychosurgery, including such modalities as the lobotomy, is recognized as a human rights abuse.[275][276] In the mid-1950s, chlorpromazine, the first typical antipsychotic, was introduced,[277] followed in the 1970s by clozapine, the first atypical antipsychotic.[278]
Political abuse
From the 1960s until 1989, psychiatrists in the USSR and Eastern Bloc diagnosed thousands of people with sluggish schizophrenia,[279][280] without signs of psychosis, based on "the assumption that symptoms would later appear".[281] Now discredited, the diagnosis provided a convenient way to confine political dissidents.[282]
Society and culture
In the United States, the annual cost of schizophrenia – including direct costs (outpatient, inpatient, drugs, and long-term care) and non-healthcare costs (law enforcement, reduced workplace productivity, and unemployment) – was estimated at $62.7 billion for the year 2002.[283][a] In the UK the cost in 2016 was put at £11.8 billion per year with a third of that figure directly attributable to the cost of hospital, social care and treatment.[7]
Stigma

In 2002, the term for schizophrenia in Japan was changed from seishin-bunretsu-byō (精神分裂病, lit. 'mind-split disease') to tōgō-shitchō-shō (統合失調症, lit. 'integration–dysregulation syndrome') to reduce stigma.[286] The new name, also interpreted as "integration disorder", was inspired by the biopsychosocial model.[287] A similar change was made in South Korea in 2012 to attunement disorder.[288]
Cultural depictions
Media coverage, especially movies, reinforce the public perception of an association between schizophrenia and violence.[289] A majority of movies have historically depicted characters with schizophrenia as criminal, dangerous, violent, unpredictable and homicidal, and depicted delusions and hallucinations as the main symptoms of schizophrenic characters, ignoring other common symptoms,[290] furthering stereotypes of schizophrenia including the idea of a split personality.[291]
The book A Beautiful Mind chronicled the life of John Forbes Nash who had been diagnosed with schizophrenia and won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. The book was made into a film with the same name; an earlier documentary film was A Brilliant Madness.
In the UK, guidelines for reporting conditions and award campaigns have shown a reduction in negative reporting since 2013.[292]
In 1964 a case study of three males diagnosed with schizophrenia who each had the delusional belief that they were Jesus Christ was published as The Three Christs of Ypsilanti; a film with the title Three Christs was released in 2020.[293][294]
Research directions
A 2015 Cochrane review found unclear evidence of benefit from brain stimulation techniques to treat the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, in particular auditory verbal hallucinations (AVHs).[295] Most studies focus on transcranial direct-current stimulation (tDCM), and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS).[296] Techniques based on focused ultrasound for deep brain stimulation could provide insight for the treatment of AVHs.[296]
The study of potential biomarkers that would help in diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia is an active area of research as of 2020. Possible biomarkers include markers of inflammation,[100] neuroimaging,[297] brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF),[298] and speech analysis. Some markers such as C-reactive protein are useful in detecting levels of inflammation implicated in some psychiatric disorders but they are not disorder-specific. Other inflammatory cytokines are found to be elevated in first episode psychosis and acute relapse that are normalized after treatment with antipsychotics, and these may be considered as state markers.[299] Deficits in sleep spindles in schizophrenia may serve as a marker of an impaired thalamocortical circuit, and a mechanism for memory impairment.[171] MicroRNAs are highly influential in early neuronal development, and their disruption is implicated in several CNS disorders; circulating microRNAs (cimiRNAs) are found in body fluids such as blood and cerebrospinal fluid, and changes in their levels are seen to relate to changes in microRNA levels in specific regions of brain tissue. These studies suggest that cimiRNAs have the potential to be early and accurate biomarkers in a number of disorders including schizophrenia.[300][301]
Ongoing fMRI research aims to identify biomarkers within these brain networks,[302] potentially aiding in earlier diagnosis and better tracking of treatment responses in schizophrenia.
Explanatory notes
References
- ^ Jones D (2003) [1917]. Roach P, Hartmann J, Setter J (eds.). English Pronouncing Dictionary. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-3-12-539683-8.
- ^ a b c d e "Schizophrenia Fact sheet". World Health Organization. 10 January 2022. Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Schizophrenia". Health topics. US National Institute of Mental Health. April 2022. Retrieved 22 August 2022.
- ^ "Medicinal treatment of psychosis/schizophrenia". Swedish Agency for Health Technology Assessment and Assessment of Social Services (SBU). 21 November 2012. Archived from the original on 29 June 2017. Retrieved 26 June 2017.
- ^ Proietto Sr J (November 2004). "Diabetes and Antipsychotic Drugs". Medsafe.
- ^ Holt RI (September 2019). "Association Between Antipsychotic Medication Use and Diabetes". Current Diabetes Reports. 19 (10). National Center for Biotechnology Information: 96. doi:10.1007/s11892-019-1220-8. ISSN 1534-4827. PMC 6718373. PMID 31478094.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Owen MJ, Sawa A, Mortensen PB (July 2016). "Schizophrenia". The Lancet. 388 (10039): 86–97. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01121-6. PMC 4940219. PMID 26777917.
- ^ "Transition of Substance-Induced, Brief, and Atypical Psychoses to Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Schizophrenia Bulletin. May 2020.
- ^ Gruebner O, Rapp MA, Adli M, Kluge U, Galea S, Heinz A (February 2017). "Cities and Mental Health". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 114 (8): 121–127. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2017.0121. PMC 5374256. PMID 28302261.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5 (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association. 2013. pp. 99–105. ISBN 978-0-89042-555-8.
- ^ a b Ferri FF (2010). "Chapter S". Ferri's differential diagnosis: a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Mosby. ISBN 978-0-323-07699-9.
- ^ a b Paris J (December 2018). "Differential Diagnosis of Borderline Personality Disorder". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 41 (4): 575–582. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2018.07.001. PMID 30447725. S2CID 53951650.
- ^ a b c d e f Laursen TM, Nordentoft M, Mortensen PB (2014). "Excess early mortality in schizophrenia". Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 10: 425–448. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032813-153657. PMID 24313570.
- ^ a b c d e "Schizophrenia". Statistics. US National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). 22 April 2022. Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- ^ "Schizophrenia Fact Sheet and Information". World Health Organization.
- ^ a b c Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, et al. (GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
- ^ "ICD-11: 6A20 Schizophrenia". World Health Organization. Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- ^ a b c d Ferri FF (2019). Ferri's clinical advisor 2019: 5 books in 1. Elsevier. pp. 1225–1226. ISBN 9780323530422.
- ^ a b Javitt DC (June 2014). "Balancing therapeutic safety and efficacy to improve clinical and economic outcomes in schizophrenia: a clinical overview". The American Journal of Managed Care. 20 (8 Suppl): S160-165. PMID 25180705.
- ^ a b James SL, Abate D (November 2018). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017". The Lancet. 392 (10159): 1789–1858. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. PMC 6227754. PMID 30496104.
- ^ a b c van de Leemput J, Hess JL, Glatt SJ, Tsuang MT (2016). Genetics of Schizophrenia: Historical Insights and Prevailing Evidence. Advances in Genetics. Vol. 96. pp. 99–141. doi:10.1016/bs.adgen.2016.08.001. ISBN 978-0-12-809672-7. PMID 27968732.
- ^ a b Parakh P, Basu D (August 2013). "Cannabis and psychosis: have we found the missing links?". Asian Journal of Psychiatry (Review). 6 (4): 281–287. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2013.03.012. PMID 23810133.
Cannabis acts as a component cause of psychosis, that is, it increases the risk of psychosis in people with certain genetic or environmental vulnerabilities, though by itself, it is neither a sufficient nor a necessary cause of psychosis.
- ^ a b Vita A, Barlati S (May 2018). "Recovery from schizophrenia: is it possible?". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 31 (3): 246–255. doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000407. PMID 29474266. S2CID 35299996.
- ^ Lawrence RE, First MB, Lieberman JA (2015). "Chapter 48: Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses". In Tasman A, Kay J, Lieberman JA, First MB, Riba MB (eds.). Psychiatry (fourth ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. pp. 798, 816, 819. doi:10.1002/9781118753378.ch48. ISBN 978-1-118-84547-9.
- ^ a b c d e Killaspy H (September 2014). "Contemporary mental health rehabilitation". East Asian Archives of Psychiatry. 24 (3): 89–94. PMID 25316799.
- ^ a b c Charlson FJ, Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Diminic S, Stockings E, Scott JG, et al. (October 2018). "Global Epidemiology and Burden of Schizophrenia: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 44 (6): 1195–1203. doi:10.1093/schbul/sby058. PMC 6192504. PMID 29762765.
- ^ a b c d e f van Os J, Kapur S (August 2009). "Schizophrenia" (PDF). Lancet. 374 (9690): 635–645. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60995-8. PMID 19700006. S2CID 208792724. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 June 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2011.
- ^ a b Hor K, Taylor M (November 2010). "Suicide and schizophrenia: a systematic review of rates and risk factors". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 24 (4 Suppl): 81–90. doi:10.1177/1359786810385490. PMC 2951591. PMID 20923923.
- ^ a b Siskind D, Siskind V, Kisely S (November 2017). "Clozapine Response Rates among People with Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Data from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 62 (11): 772–777. doi:10.1177/0706743717718167. PMC 5697625. PMID 28655284.
- ^ Leucht S, Cipriani A, Spineli L, Mavridis D, Orey D, Richter F, et al. (September 2013). "Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis". Lancet. 382 (9896): 951–962. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60733-3. PMID 23810019. S2CID 32085212.
- ^ a b Becker T, Kilian R (2006). "Psychiatric services for people with severe mental illness across western Europe: what can be generalized from current knowledge about differences in provision, costs and outcomes of mental health care?". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. Supplementum. 113 (429): 9–16. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2005.00711.x. PMID 16445476. S2CID 34615961.
- ^ a b c Capdevielle D, Boulenger JP, Villebrun D, Ritchie K (September 2009). "Durées d'hospitalisation des patients souffrant de schizophrénie: implication des systèmes de soin et conséquences médicoéconomiques" [Schizophrenic patients' length of stay: mental health care implication and medicoeconomic consequences]. L'Encéphale (in French). 35 (4): 394–399. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2008.11.005. PMID 19748377.
- ^ a b Narayan KK, Kumar DS (January 2012). "Disability in a Group of Long-stay Patients with Schizophrenia: Experience from a Mental Hospital". Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine. 34 (1): 70–75. doi:10.4103/0253-7176.96164. PMC 3361848. PMID 22661812.
- ^ a b c "Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: treatment and management" (PDF). National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). March 2014. pp. 4–34. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 April 2014. Retrieved 19 April 2014.
- ^ Stępnicki P, Kondej M, Kaczor AA (20 August 2018). "Current Concepts and Treatments of Schizophrenia". Molecules. 23 (8): 2087. doi:10.3390/molecules23082087. PMC 6222385. PMID 30127324.
- ^ a b c d "RAISE Questions and Answers". US National Institute of Mental Health. Retrieved 29 December 2019.
- ^ Marshall M (September 2005). "Association between duration of untreated psychosis and outcome in cohorts of first-episode patients: a systematic review". Archives of General Psychiatry. 62 (9): 975–983. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.62.9.975. PMID 16143729. S2CID 13504781.
- ^ a b Montagnese M, Leptourgos P, Fernyhough C, et al. (January 2021). "A Review of Multimodal Hallucinations: Categorization, Assessment, Theoretical Perspectives, and Clinical Recommendations". Schizophr Bull. 47 (1): 237–248. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbaa101. PMC 7825001. PMID 32772114.
- ^ Császár N, Kapócs G, Bókkon I (27 May 2019). "A possible key role of vision in the development of schizophrenia". Reviews in the Neurosciences. 30 (4): 359–379. doi:10.1515/revneuro-2018-0022 (inactive 3 December 2024). PMID 30244235. S2CID 52813070.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of December 2024 (link) - ^ a b American Psychiatric Association. Task Force on DSM-IV. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV-TR. American Psychiatric Pub. pp. 299–304. ISBN 978-0-89042-025-6.
- ^ a b Heinz A, Voss M, Lawrie SM, Mishara A, Bauer M, Gallinat J, et al. (September 2016). "Shall we really say goodbye to first rank symptoms?". European Psychiatry. 37: 8–13. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2016.04.010. PMID 27429167. S2CID 13761854.
- ^ a b Adida M, Azorin JM, Belzeaux R, Fakra E (December 2015). "[Negative Symptoms: Clinical and Psychometric Aspects]". L'Encephale. 41 (6 Suppl 1): 6S15–17. doi:10.1016/S0013-7006(16)30004-5. PMID 26776385.
- ^ Mach C, Dollfus S (April 2016). "[Scale for Assessing Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review]". L'Encephale. 42 (2): 165–171. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2015.12.020. PMID 26923997.
- ^ Waltz JA, Gold JM (2016). "Motivational Deficits in Schizophrenia and the Representation of Expected Value". Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 27: 375–410. doi:10.1007/7854_2015_385. ISBN 978-3-319-26933-7. PMC 4792780. PMID 26370946.
- ^ a b Husain M, Roiser JP (August 2018). "Neuroscience of apathy and anhedonia: a transdiagnostic approach". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 19 (8): 470–484. doi:10.1038/s41583-018-0029-9. PMID 29946157. S2CID 49428707.
- ^ a b Galderisi S, Mucci A, Buchanan RW, Arango C (August 2018). "Negative symptoms of schizophrenia: new developments and unanswered research questions". The Lancet. Psychiatry. 5 (8): 664–677. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30050-6. PMID 29602739. S2CID 4483198.
- ^ Klaus F, Dorsaz O, Kaiser S (19 September 2018). "[Negative symptoms in schizophrenia – overview and practical implications]". Revue médicale suisse. 14 (619): 1660–1664. doi:10.53738/REVMED.2018.14.619.1660. PMID 30230774. S2CID 246764656.
- ^ Batinic B (June 2019). "Cognitive Models of Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia and Implications for Treatment". Psychiatria Danubina. 31 (Suppl 2): 181–184. PMID 31158119.
- ^ Bortolon C, Macgregor A, Capdevielle D, Raffard S (September 2018). "Apathy in schizophrenia: A review of neuropsychological and neuroanatomical studies". Neuropsychologia. 118 (Pt B): 22–33. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.09.033. PMID 28966139. S2CID 13411386.
- ^ a b c d e Marder SR, Kirkpatrick B (May 2014). "Defining and measuring negative symptoms of schizophrenia in clinical trials". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 24 (5): 737–743. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.10.016. PMID 24275698. S2CID 5172022.
- ^ a b c Tatsumi K, Kirkpatrick B, Strauss GP, Opler M (April 2020). "The brief negative symptom scale in translation: A review of psychometric properties and beyond". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 33: 36–44. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2020.01.018. PMID 32081498. S2CID 211141678.
- ^ Klaus F, Kaiser S, Kirschner M (June 2018). "[Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia – an Overview]". Therapeutische Umschau. 75 (1): 51–56. doi:10.1024/0040-5930/a000966. PMID 29909762. S2CID 196502392.
- ^ Lindenmayer JP, Nasrallah H, Pucci M, James S, Citrome L (1 July 2013). "A systematic review of psychostimulant treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia: Challenges and therapeutic opportunities". Schizophrenia Research. 147 (2): 241–252. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2013.03.019. ISSN 0920-9964. PMID 23619055.
- ^ Wójciak P, Rybakowski J (30 April 2018). "Clinical picture, pathogenesis and psychometric assessment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia". Psychiatria Polska. 52 (2): 185–197. doi:10.12740/PP/70610. PMID 29975360.
- ^ a b c d e f Murante T, Cohen CI (January 2017). "Cognitive Functioning in Older Adults With Schizophrenia". Focus (American Psychiatric Publishing). 15 (1): 26–34. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20160032. PMC 6519630. PMID 31975837.
- ^ a b Kar SK, Jain M (July 2016). "Current understandings about cognition and the neurobiological correlates in schizophrenia". Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice. 7 (3): 412–418. doi:10.4103/0976-3147.176185. PMC 4898111. PMID 27365960.
- ^ a b Bozikas VP, Andreou C (February 2011). "Longitudinal studies of cognition in first episode psychosis: a systematic review of the literature". The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 45 (2): 93–108. doi:10.3109/00048674.2010.541418. PMID 21320033. S2CID 26135485.
- ^ Shah JN, Qureshi SU, Jawaid A, Schulz PE (June 2012). "Is there evidence for late cognitive decline in chronic schizophrenia?". The Psychiatric Quarterly. 83 (2): 127–144. doi:10.1007/s11126-011-9189-8. PMID 21863346. S2CID 10970088.
- ^ a b c Biedermann F, Fleischhacker WW (August 2016). "Psychotic disorders in DSM-5 and ICD-11". CNS Spectrums. 21 (4): 349–354. doi:10.1017/S1092852916000316. PMID 27418328. S2CID 24728447.
- ^ a b c Vidailhet P (September 2013). "[First-episode psychosis, cognitive difficulties and remediation]". L'Encéphale (in French). 39 (Suppl 2): S83-92. doi:10.1016/S0013-7006(13)70101-5. PMID 24084427.
- ^ a b c Hashimoto K (5 July 2019). "Recent Advances in the Early Intervention in Schizophrenia: Future Direction from Preclinical Findings". Current Psychiatry Reports. 21 (8): 75. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1063-7. PMID 31278495. S2CID 195814019.
- ^ a b c d e f Green MF, Horan WP, Lee J (June 2019). "Nonsocial and social cognition in schizophrenia: current evidence and future directions". World Psychiatry. 18 (2): 146–161. doi:10.1002/wps.20624. PMC 6502429. PMID 31059632.
- ^ Javitt DC, Sweet RA (September 2015). "Auditory dysfunction in schizophrenia: integrating clinical and basic features". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 16 (9): 535–550. doi:10.1038/nrn4002. PMC 4692466. PMID 26289573.
- ^ a b Megreya AM (2016). "Face perception in schizophrenia: a specific deficit". Cognitive Neuropsychiatry. 21 (1): 60–72. doi:10.1080/13546805.2015.1133407. PMID 26816133. S2CID 26125559.
- ^ Eack SM (July 2012). "Cognitive remediation: a new generation of psychosocial interventions for people with schizophrenia". Social Work. 57 (3): 235–246. doi:10.1093/sw/sws008. PMC 3683242. PMID 23252315.
- ^ Pomarol-Clotet E, Oh M, Laws KR, McKenna PJ (February 2008). "Semantic priming in schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 192 (2): 92–97. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.106.032102. hdl:2299/2735. PMID 18245021.
- ^ Goldberg TE, Keefe RS, Goldman RS, Robinson DG, Harvey PD (April 2010). "Circumstances under which practice does not make perfect: a review of the practice effect literature in schizophrenia and its relevance to clinical treatment studies". Neuropsychopharmacology. 35 (5): 1053–1062. doi:10.1038/npp.2009.211. PMC 3055399. PMID 20090669.
- ^ King DJ, Hodgekins J, Chouinard PA, Chouinard VA, Sperandio I (June 2017). "A review of abnormalities in the perception of visual illusions in schizophrenia". Psychonomic Bulletin and Review. 24 (3): 734–751. doi:10.3758/s13423-016-1168-5. PMC 5486866. PMID 27730532.
- ^ Kohler CG, Walker JB, Martin EA, Healey KM, Moberg PJ (September 2010). "Facial emotion perception in schizophrenia: a meta-analytic review". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 36 (5): 1009–1019. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbn192. PMC 2930336. PMID 19329561.
- ^ Le Gall E, Iakimova G (December 2018). "[Social cognition in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder: Points of convergence and functional differences]". L'Encéphale. 44 (6): 523–537. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2018.03.004. PMID 30122298. S2CID 150099236.
- ^ Grill-Spector K, Weiner KS, Kay K, Gomez J (September 2017). "The Functional Neuroanatomy of Human Face Perception". Annual Review of Vision Science. 3: 167–196. doi:10.1146/annurev-vision-102016-061214. PMC 6345578. PMID 28715955.
- ^ Fountoulakis KN, Panagiotidis P, Kimiskidis V, Nimatoudis I, Gonda X (February 2019). "Neurological soft signs in familial and sporadic schizophrenia". Psychiatry Research. 272: 222–229. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.105. PMID 30590276. S2CID 56476015.
- ^ Bourgou Gaha S, Halayem Dhouib S, Amado I, Bouden A (June 2015). "[Neurological soft signs in early onset schizophrenia]". L'Encephale. 41 (3): 209–214. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2014.01.005. PMID 24854724.
- ^ a b Da Fonseca D, Fourneret P (December 2018). "[Very early onset schizophrenia]". L'Encephale. 44 (6S): S8 – S11. doi:10.1016/S0013-7006(19)30071-5. PMID 30935493. S2CID 150798223.
- ^ Häfner H (2019). "From Onset and Prodromal Stage to a Life-Long Course of Schizophrenia and Its Symptom Dimensions: How Sex, Age, and Other Risk Factors Influence Incidence and Course of Illness". Psychiatry Journal. 2019: 9804836. doi:10.1155/2019/9804836. PMC 6500669. PMID 31139639.
- ^ Cohen CI, Freeman K, Ghoneim D, Vengassery A, Ghezelaiagh B, Reinhardt MM (March 2018). "Advances in the Conceptualization and Study of Schizophrenia in Later Life". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 41 (1): 39–53. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2017.10.004. PMID 29412847.
- ^ a b c George M, Maheshwari S, Chandran S, Manohar JS, Sathyanarayana Rao TS (October 2017). "Understanding the schizophrenia prodrome". Indian Journal of Psychiatry. 59 (4): 505–509. doi:10.4103/psychiatry.IndianJPsychiatry_464_17 (inactive 1 November 2024). PMC 5806335. PMID 29497198.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ a b Conroy S, Francis M, Hulvershorn LA (March 2018). "Identifying and treating the prodromal phases of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia". Current Treatment Options in Psychiatry. 5 (1): 113–128. doi:10.1007/s40501-018-0138-0. PMC 6196741. PMID 30364516.
- ^ Lecardeur L, Meunier-Cussac S, Dollfus S (May 2013). "[Cognitive deficits in first episode psychosis patients and people at risk for psychosis: from diagnosis to treatment]". L'Encephale. 39 (Suppl 1): S64-71. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2012.10.011. PMID 23528322.
- ^ Mullin AP, Gokhale A, Moreno-De-Luca A, Sanyal S, Waddington JL, Faundez V (December 2013). "Neurodevelopmental disorders: mechanisms and boundary definitions from genomes, interactomes and proteomes". Translational Psychiatry. 3 (12): e329. doi:10.1038/tp.2013.108. PMC 4030327. PMID 24301647.
- ^ a b c Davis J, Eyre H, Jacka FN, Dodd S, Dean O, McEwen S, et al. (June 2016). "A review of vulnerability and risks for schizophrenia: Beyond the two hit hypothesis". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 65: 185–194. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.017. PMC 4876729. PMID 27073049.
- ^ a b Perkovic MN, Erjavec GN, Strac DS, Uzun S, Kozumplik O, Pivac N (March 2017). "Theranostic Biomarkers for Schizophrenia". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 18 (4): 733. doi:10.3390/ijms18040733. PMC 5412319. PMID 28358316.
- ^ a b Suvisaari J (2010). "[Risk factors of schizophrenia]". Duodecim; Laaketieteellinen Aikakauskirja (in Finnish). 126 (8): 869–876. PMID 20597333.
- ^ a b Combs DR, Mueser KT, Gutierrez MM (2011). "Chapter 8: Schizophrenia: Etiological considerations". In Hersen M, Beidel DC (eds.). Adult psychopathology and diagnosis (6th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-118-13884-7.
- ^ O'Donovan MC, Williams NM, Owen MJ (October 2003). "Recent advances in the genetics of schizophrenia". Human Molecular Genetics. 12 Spec No 2: R125–133. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg302. PMID 12952866.
- ^ a b Torrey EF, Yolken RH (August 2019). "Schizophrenia as a pseudogenetic disease: A call for more gene-environmental studies". Psychiatry Research. 278: 146–150. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2019.06.006. PMID 31200193. S2CID 173991937.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Picchioni MM, Murray RM (July 2007). "Schizophrenia". BMJ. 335 (7610): 91–95. doi:10.1136/bmj.39227.616447.BE. PMC 1914490. PMID 17626963.
- ^ Farrell MS, Werge T, Sklar P, Owen MJ, Ophoff RA, O'Donovan MC, et al. (May 2015). "Evaluating historical candidate genes for schizophrenia". Molecular Psychiatry. 20 (5): 555–562. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.16. PMC 4414705. PMID 25754081.
- ^ Schulz SC, Green MF, Nelson KJ (2016). Schizophrenia and Psychotic Spectrum Disorders. Oxford University Press. pp. 124–125. ISBN 9780199378067.
- ^ Schork AJ, Wang Y, Thompson WK, Dale AM, Andreassen OA (February 2016). "New statistical approaches exploit the polygenic architecture of schizophrenia—implications for the underlying neurobiology". Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 36: 89–98. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2015.10.008. PMC 5380793. PMID 26555806.
- ^ Coelewij L, Curtis D (2018). "Mini-review: Update on the genetics of schizophrenia". Annals of Human Genetics. 82 (5): 239–243. doi:10.1111/ahg.12259. ISSN 0003-4800. PMID 29923609. S2CID 49311660.
- ^ Kendler KS (March 2016). "The Schizophrenia Polygenic Risk Score: To What Does It Predispose in Adolescence?". JAMA Psychiatry. 73 (3): 193–194. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2964. PMID 26817666.
- ^ a b Lowther C, Costain G, Baribeau DA, Bassett AS (September 2017). "Genomic Disorders in Psychiatry—What Does the Clinician Need to Know?". Current Psychiatry Reports. 19 (11): 82. doi:10.1007/s11920-017-0831-5. PMID 28929285. S2CID 4776174.
- ^ Bundy H, Stahl D, MacCabe JH (February 2011). "A systematic review and meta-analysis of the fertility of patients with schizophrenia and their unaffected relatives: Fertility in schizophrenia". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 123 (2): 98–106. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2010.01623.x. PMID 20958271. S2CID 45179016.
- ^ van Dongen J, Boomsma DI (March 2013). "The evolutionary paradox and the missing heritability of schizophrenia". American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics. 162 (2): 122–136. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32135. PMID 23355297. S2CID 9648115.
- ^ Owen MJ, Sawa A, Mortensen PB (2 July 2016). "Schizophrenia". Lancet. 388 (10039): 86–97. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01121-6. PMC 4940219. PMID 26777917.
- ^ Goh XX, Tang PY, Tee SF (July 2021). "8-Hydroxy-2'-Deoxyguanosine and Reactive Oxygen Species as Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Mental Illnesses: A Meta-Analysis". Psychiatry Investig (Meta-analysis). 18 (7): 603–618. doi:10.30773/pi.2020.0417. PMC 8328836. PMID 34340273.
- ^ Stilo SA, Murray RM (14 September 2019). "Non-Genetic Factors in Schizophrenia". Current Psychiatry Reports. 21 (10): 100. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1091-3. PMC 6745031. PMID 31522306.
- ^ Cirulli F, Musillo C, Berry A (5 February 2020). "Maternal Obesity as a Risk Factor for Brain Development and Mental Health in the Offspring". Neuroscience. 447: 122–135. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.01.023. hdl:11573/1387747. PMID 32032668. S2CID 211029692.
- ^ a b Upthegrove R, Khandaker GM (2020). "Cytokines, Oxidative Stress and Cellular Markers of Inflammation in Schizophrenia" (PDF). Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 44: 49–66. doi:10.1007/7854_2018_88. ISBN 978-3-030-39140-9. PMID 31115797. S2CID 162169817.
- ^ a b Chiang M, Natarajan R, Fan X (February 2016). "Vitamin D in schizophrenia: a clinical review". Evidence-Based Mental Health. 19 (1): 6–9. doi:10.1136/eb-2015-102117. PMC 10699337. PMID 26767392. S2CID 206926835.
- ^ Arias I, Sorlozano A, Villegas E, de Dios Luna J, McKenney K, Cervilla J, et al. (April 2012). "Infectious agents associated with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis". Schizophrenia Research. 136 (1–3): 128–136. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2011.10.026. hdl:10481/90076. PMID 22104141. S2CID 2687441.
- ^ Yolken R (June 2004). "Viruses and schizophrenia: a focus on herpes simplex virus". Herpes. 11 (Suppl 2): 83A – 88A. PMID 15319094.
- ^ Khandaker GM (August 2012). "Childhood infection and adult schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of population-based studies". Schizophr. Res. 139 (1–3): 161–168. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2012.05.023. PMC 3485564. PMID 22704639.
- ^ McGrath JJ, Lim CC, Saha S (May 2024). "Cat Ownership and Schizophrenia-Related Disorders and Psychotic-Like Experiences: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 50 (3): 489–495. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbad168. PMC 11059805. PMID 38491934.
- ^ a b Pearce J, Murray C, Larkin W (July 2019). "Childhood adversity and trauma:experiences of professionals trained to routinely enquire about childhood adversity". Heliyon. 5 (7): e01900. Bibcode:2019Heliy...501900P. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01900. PMC 6658729. PMID 31372522.
- ^ Dvir Y, Denietolis B, Frazier JA (October 2013). "Childhood trauma and psychosis". Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 22 (4): 629–641. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2013.04.006. PMID 24012077. S2CID 40053289.
- ^ Misiak B, Krefft M, Bielawski T, Moustafa AA, Sąsiadek MM, Frydecka D (April 2017). "Toward a unified theory of childhood trauma and psychosis: A comprehensive review of epidemiological, clinical, neuropsychological and biological findings". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 75: 393–406. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.02.015. PMID 28216171. S2CID 21614845.
- ^ a b Nettis MA, Pariante CM, Mondelli V (2020). "Early-Life Adversity, Systemic Inflammation and Comorbid Physical and Psychiatric Illnesses of Adult Life". Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 44: 207–225. doi:10.1007/7854_2019_89. ISBN 978-3-030-39140-9. PMID 30895531. S2CID 84842249.
- ^ Guloksuz S, van Os J (January 2018). "The slow death of the concept of schizophrenia and the painful birth of the psychosis spectrum". Psychological Medicine. 48 (2): 229–244. doi:10.1017/S0033291717001775. PMID 28689498.
- ^ Costa E, Silva JA, Steffen RE (November 2019). "Urban environment and psychiatric disorders: a review of the neuroscience and biology". Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental. 100S: 153940. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2019.07.004. PMID 31610855. S2CID 204704312.
- ^ van Os J (April 2004). "Does the urban environment cause psychosis?". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 184 (4): 287–8. doi:10.1192/bjp.184.4.287. PMID 15056569.
- ^ Attademo L, Bernardini F, Garinella R, Compton MT (March 2017). "Environmental pollution and risk of psychotic disorders: A review of the science to date". Schizophrenia Research. 181: 55–59. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2016.10.003. PMID 27720315. S2CID 25505446.
- ^ Selten JP, Cantor-Graae E, Kahn RS (March 2007). "Migration and schizophrenia". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 20 (2): 111–115. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e328017f68e. PMID 17278906. S2CID 21391349.
- ^ Sharma R, Agarwal A, Rohra VK, Assidi M, Abu-Elmagd M, Turki RF (April 2015). "Effects of increased paternal age on sperm quality, reproductive outcome and associated epigenetic risks to offspring". Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology. 13: 35. doi:10.1186/s12958-015-0028-x. PMC 4455614. PMID 25928123.
- ^ a b Gregg L, Barrowclough C, Haddock G (May 2007). "Reasons for increased substance use in psychosis". Clinical Psychology Review. 27 (4): 494–510. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2006.09.004. PMID 17240501.
- ^ Sagud M, Mihaljević-Peles A, Mück-Seler D, Pivac N, Vuksan-Cusa B, Brataljenović T, et al. (September 2009). "Smoking and schizophrenia". Psychiatria Danubina. 21 (3): 371–375. PMID 19794359.
- ^ Larson M (30 March 2006). "Alcohol-Related Psychosis". EMedicine. Archived from the original on 9 November 2008. Retrieved 27 September 2006.
- ^ Leweke FM, Koethe D (June 2008). "Cannabis and psychiatric disorders: it is not only addiction". Addiction Biology. 13 (2): 264–75. doi:10.1111/j.1369-1600.2008.00106.x. PMID 18482435. S2CID 205400285.
- ^ a b c d Khokhar JY, Henricks AM, Sullivan ED, Green AI (2018). "Unique Effects of Clozapine: A Pharmacological Perspective". Apprentices to Genius: A tribute to Solomon H. Snyder. Advances in Pharmacology. Vol. 82. pp. 137–162. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2017.09.009. ISBN 978-0128140871. PMC 7197512. PMID 29413518.
- ^ Bighelli I, Rodolico A, García-Mieres H, et al. (November 2021). "Psychosocial and psychological interventions for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis" (PDF). Lancet Psychiatry. 8 (11): 969–980. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00243-1. PMID 34653393. S2CID 239003358.
- ^ Patel S, Khan S, M S, Hamid P (July 2020). "The Association Between Cannabis Use and Schizophrenia: Causative or Curative? A Systematic Review". Cureus. 12 (7): e9309. doi:10.7759/cureus.9309. PMC 7442038. PMID 32839678.
- ^ Hasan A, von Keller R, Friemel CM, Hall W, Schneider M, Koethe D, et al. (June 2020). "Cannabis use and psychosis: a review of reviews". Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 270 (4): 403–412. doi:10.1007/s00406-019-01068-z. PMID 31563981. S2CID 203567900.
- ^ "Causes — Schizophrenia". UK National Health Service. 11 November 2019. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ Ortiz-Medina MB, Perea M, Torales J, Ventriglio A, Vitrani G, Aguilar L, et al. (November 2018). "Cannabis consumption and psychosis or schizophrenia development". The International Journal of Social Psychiatry. 64 (7): 690–704. doi:10.1177/0020764018801690. PMID 30442059. S2CID 53563635.
- ^ Hayes D, Kyriakopoulos M (August 2018). "Dilemmas in the treatment of early-onset first-episode psychosis". Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology. 8 (8): 231–239. doi:10.1177/2045125318765725. PMC 6058451. PMID 30065814.
- ^ Cannon TD (December 2015). "How Schizophrenia Develops: Cognitive and Brain Mechanisms Underlying Onset of Psychosis". Trends Cogn Sci. 19 (12): 744–756. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2015.09.009. PMC 4673025. PMID 26493362.
- ^ Correll CU, Schooler NR (2020). "Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia: A Review and Clinical Guide for Recognition, Assessment, and Treatment". Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 16: 519–534. doi:10.2147/NDT.S225643. PMC 7041437. PMID 32110026.
- ^ Howes OD (1 January 2017). "The Role of Genes, Stress, and Dopamine in the Development of Schizophrenia". Biological Psychiatry. 81 (1): 9–20. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.07.014. PMC 5675052. PMID 27720198.
- ^ Broyd A, Balzan RP, Woodward TS, Allen P (June 2017). "Dopamine, cognitive biases and assessment of certainty: A neurocognitive model of delusions". Clinical Psychology Review. 54: 96–106. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2017.04.006. PMID 28448827. S2CID 3729566.
- ^ Howes OD, Murray RM (May 2014). "Schizophrenia: an integrated sociodevelopmental-cognitive model". Lancet. 383 (9929): 1677–1687. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62036-X. PMC 4127444. PMID 24315522.
- ^ Grace AA (August 2016). "Dysregulation of the dopamine system in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and depression". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 17 (8): 524–532. doi:10.1038/nrn.2016.57. PMC 5166560. PMID 27256556.
- ^ Fusar-Poli P, Meyer-Lindenberg A (January 2013). "Striatal presynaptic dopamine in schizophrenia, part II: meta-analysis of [(18)F/(11)C]-DOPA PET studies". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 39 (1): 33–42. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbr180. PMC 3523905. PMID 22282454.
- ^ Howes OD, Kambeitz J, Kim E, Stahl D, Slifstein M, Abi-Dargham A, et al. (August 2012). "The nature of dopamine dysfunction in schizophrenia and what this means for treatment". Archives of General Psychiatry. 69 (8): 776–786. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.169. PMC 3730746. PMID 22474070.
- ^ Arnsten AF, Girgis RR, Gray DL, Mailman RB (January 2017). "Novel Dopamine Therapeutics for Cognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia". Biological Psychiatry. 81 (1): 67–77. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.12.028. PMC 4949134. PMID 26946382.
- ^ Maia TV, Frank MJ (January 2017). "An Integrative Perspective on the Role of Dopamine in Schizophrenia". Biological Psychiatry. 81 (1): 52–66. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.05.021. PMC 5486232. PMID 27452791.
- ^ a b Pratt J, Dawson N, Morris BJ, Grent-'t-Jong T, Roux F, Uhlhaas PJ (February 2017). "Thalamo-cortical communication, glutamatergic neurotransmission and neural oscillations: A unique window into the origins of ScZ?" (PDF). Schizophrenia Research. 180: 4–12. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2016.05.013. PMID 27317361. S2CID 205075178.
- ^ Catts VS, Lai YL, Weickert CS, Weickert TW, Catts SV (April 2016). "A quantitative review of the post-mortem evidence for decreased cortical N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor expression levels in schizophrenia: How can we link molecular abnormalities to mismatch negativity deficits?". Biological Psychology. 116: 57–67. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2015.10.013. PMID 26549579.
- ^ Michie PT, Malmierca MS, Harms L, Todd J (April 2016). "The neurobiology of MMN and implications for schizophrenia". Biological Psychology. 116: 90–97. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2016.01.011. PMID 26826620. S2CID 41179430.
- ^ a b Marín O (January 2012). "Interneuron dysfunction in psychiatric disorders". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 13 (2): 107–120. doi:10.1038/nrn3155. PMID 22251963. S2CID 205507186.
- ^ Lewis DA, Hashimoto T, Volk DW (April 2005). "Cortical inhibitory neurons and schizophrenia". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 6 (4): 312–324. doi:10.1038/nrn1648. PMID 15803162. S2CID 3335493.
- ^ Senkowski D, Gallinat J (June 2015). "Dysfunctional prefrontal gamma-band oscillations reflect working memory and other cognitive deficits in schizophrenia". Biological Psychiatry. 77 (12): 1010–1019. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.02.034. PMID 25847179. S2CID 206104940.
Several studies that investigated perceptual processes found impaired GBR in ScZ patients over sensory areas, such as the auditory and visual cortex. Moreover, studies examining steady-state auditory-evoked potentials showed deficits in the gen- eration of oscillations in the gamma band.
- ^ Reilly TJ, Nottage JF, Studerus E, Rutigliano G, Micheli AI, Fusar-Poli P, et al. (July 2018). "Gamma band oscillations in the early phase of psychosis: A systematic review". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 90: 381–399. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.04.006. PMID 29656029. S2CID 4891072.
Decreased gamma power in response to a task was a relatively consistent finding, with 5 out of 6 studies reported reduced evoked or induced power.
- ^ a b Sloan SA, Barres BA (August 2014). "Mechanisms of astrocyte development and their contributions to neurodevelopmental disorders". Curr Opin Neurobiol. 27: 75–81. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2014.03.005. PMC 4433289. PMID 24694749.
- ^ Lesh TA, Niendam TA, Minzenberg MJ, Carter CS (January 2011). "Cognitive control deficits in schizophrenia: mechanisms and meaning". Neuropsychopharmacology. 36 (1): 316–338. doi:10.1038/npp.2010.156. PMC 3052853. PMID 20844478.
- ^ Barch DM, Ceaser A (January 2012). "Cognition in schizophrenia: core psychological and neural mechanisms". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 16 (1): 27–34. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2011.11.015. PMC 3860986. PMID 22169777.
- ^ Eisenberg DP, Berman KF (January 2010). "Executive function, neural circuitry, and genetic mechanisms in schizophrenia". Neuropsychopharmacology. 35 (1): 258–277. doi:10.1038/npp.2009.111. PMC 2794926. PMID 19693005.
- ^ Walton E, Hibar DP, van Erp TG, Potkin SG, Roiz-Santiañez R, Crespo-Facorro B, et al. (May 2017). "Positive symptoms associate with cortical thinning in the superior temporal gyrus via the ENIGMA Schizophrenia consortium". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 135 (5): 439–447. doi:10.1111/acps.12718. PMC 5399182. PMID 28369804.
- ^ Walton E, Hibar DP, van Erp TG, Potkin SG, Roiz-Santiañez R, Crespo-Facorro B, et al. (Karolinska Schizophrenia Project Consortium (KaSP)) (January 2018). "Prefrontal cortical thinning links to negative symptoms in schizophrenia via the ENIGMA consortium". Psychological Medicine. 48 (1): 82–94. doi:10.1017/S0033291717001283. PMC 5826665. PMID 28545597.
- ^ Cohen AS, Minor KS (January 2010). "Emotional experience in patients with schizophrenia revisited: meta-analysis of laboratory studies". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 36 (1): 143–150. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbn061. PMC 2800132. PMID 18562345.
- ^ Strauss GP, Gold JM (April 2012). "A new perspective on anhedonia in schizophrenia". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 169 (4): 364–373. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11030447. PMC 3732829. PMID 22407079.
- ^ Young J, Anticevic A, Barch D (2018). "Cognitive and Motivational Neuroscience of Psychotic Disorders". In Charney D, Buxbaum J, Sklar P, Nestler E (eds.). Charney & Nestler's Neurobiology of Mental Illness (5th ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 215, 217. ISBN 9780190681425.
Several recent reviews (e.g., Cohen and Minor, 2010) have found that individuals with schizophrenia show relatively intact self-reported emotional responses to affect-eliciting stimuli as well as other indicators of intact response(215)...Taken together, the literature increasingly suggests that there may be a deficit in putatively DA-mediated reward learning and/ or reward prediction functions in schizophrenia. Such findings suggest that impairment in striatal reward prediction mechanisms may influence "wanting" in schizophrenia in a way that reduces the ability of individuals with schizophrenia to use anticipated rewards to drive motivated behavior.(217)
- ^ a b Wiberg A, Ng M, Al Omran Y, Alfaro-Almagro F, McCarthy P, Marchini J, et al. (October 2019). "Handedness, language areas and neuropsychiatric diseases: insights from brain imaging and genetics". Brain. 142 (10): 2938–2947. doi:10.1093/brain/awz257. PMC 6763735. PMID 31504236.
- ^ Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Kennedy H, Van Essen DC, Christen Y (2016). "Intra- and Inter-hemispheric Connectivity Supporting Hemispheric Specialization". Micro-, Meso- and Macro-Connectomics of the Brain. Research and Perspectives in Neurosciences. pp. 129–146. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-27777-6_9. ISBN 978-3-319-27776-9. PMID 28590670. S2CID 147813648.
- ^ Ocklenburg S, Güntürkün O, Hugdahl K, Hirnstein M (December 2015). "Laterality and mental disorders in the postgenomic age—A closer look at schizophrenia and language lateralization". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 59: 100–110. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.08.019. PMID 26598216. S2CID 15983622.
- ^ Friston KJ, Stephan KE, Montague R, Dolan RJ (July 2014). "Computational psychiatry: the brain as a phantastic organ". The Lancet. Psychiatry. 1 (2): 148–158. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(14)70275-5. PMID 26360579. S2CID 15504512.
- ^ Griffin JD, Fletcher PC (May 2017). "Predictive Processing, Source Monitoring, and Psychosis". Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 13: 265–289. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032816-045145. PMC 5424073. PMID 28375719.
- ^ Fletcher PC, Frith CD (January 2009). "Perceiving is believing: a Bayesian approach to explaining the positive symptoms of schizophrenia" (PDF). Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 10 (1): 48–58. doi:10.1038/nrn2536. PMID 19050712. S2CID 6219485.
- ^ Corlett PR, Taylor JR, Wang XJ, Fletcher PC, Krystal JH (November 2010). "Toward a neurobiology of delusions". Progress in Neurobiology. 92 (3): 345–369. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.06.007. PMC 3676875. PMID 20558235.
- ^ Bastos AM, Usrey WM, Adams RA, Mangun GR, Fries P, Friston KJ (November 2012). "Canonical microcircuits for predictive coding". Neuron. 76 (4): 695–711. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.038. PMC 3777738. PMID 23177956.
- ^ Soltan M, Girguis J (8 May 2017). "How to approach the mental state examination". BMJ. 357: j1821. doi:10.1136/sbmj.j1821. PMID 31055448. S2CID 145820368. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- ^ Lindenmayer JP (1 December 2017). "Are Shorter Versions of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Doable? A Critical Review". Innovations in Clinical Neuroscience. 14 (11–12): 73–76. PMC 5788254. PMID 29410940.
- ^ "Diagnosis of schizophrenia". Australian Department of Health. 10 January 2019. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ^ "Schizophrenia – Diagnosis". UK National Health Service. 23 October 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ^ Jakobsen KD, Frederiksen JN, Hansen T, Jansson LB, Parnas J, Werge T (2005). "Reliability of clinical ICD-10 schizophrenia diagnoses". Nordic Journal of Psychiatry. 59 (3): 209–212. doi:10.1080/08039480510027698. PMID 16195122. S2CID 24590483.
- ^ Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Ford JM (27 April 2012). "Default Mode Network Activity and Connectivity in Psychopathology". Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 8 (1): 49–76. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143049. ISSN 1548-5943. PMID 22224834.
- ^ Menon V (October 2011). "Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 15 (10): 483–506. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.003. PMID 21908230.
- ^ Baker JT, Holmes AJ, Masters GA, Yeo BT, Krienen F, Buckner RL, et al. (1 February 2014). "Disruption of Cortical Association Networks in Schizophrenia and Psychotic Bipolar Disorder". JAMA Psychiatry. 71 (2): 109–118. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.3469. ISSN 2168-622X. PMC 4435541. PMID 24306091.
- ^ a b c Richard-Devantoy S, Olie JP, Gourevitch R (December 2009). "[Risk of homicide and major mental disorders: a critical review]". L'Encephale. 35 (6): 521–530. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2008.10.009. PMID 20004282.
- ^ a b Staedt J, Hauser M, Gudlowski Y, Stoppe G (February 2010). "Sleep disorders in schizophrenia". Fortschritte der Neurologie-Psychiatrie. 78 (2): 70–80. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1109967. PMID 20066610. S2CID 260137215.
- ^ a b Pocivavsek A, Rowland LM (13 January 2018). "Basic Neuroscience Illuminates Causal Relationship Between Sleep and Memory: Translating to Schizophrenia". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 44 (1): 7–14. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbx151. PMC 5768044. PMID 29136236.
- ^ a b Monti JM, BaHammam AS, Pandi-Perumal SR, Bromundt V, Spence DW, Cardinali DP, et al. (June 2013). "Sleep and circadian rhythm dysregulation in schizophrenia". Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry. 43: 209–216. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.12.021. hdl:11336/3858. PMID 23318689. S2CID 19626589.
- ^ Faulkner SM, Bee PE, Meyer N, Dijk DJ, Drake RJ (August 2019). "Light therapies to improve sleep in intrinsic circadian rhythm sleep disorders and neuro-psychiatric illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Sleep Medicine Reviews. 46: 108–123. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2019.04.012. PMID 31108433.
- ^ Assimakopoulos K, Karaivazoglou K, Skokou M, Kalogeropoulou M, Kolios P, Gourzis P, et al. (March 2018). "Genetic Variations Associated with Sleep Disorders in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review". Medicines. 5 (2): 27. doi:10.3390/medicines5020027. PMC 6023503. PMID 29587340.
- ^ Dieset I, Andreassen O, Haukvik U (2016). "Somatic Comorbidity in Schizophrenia: Some Possible Biological Mechanisms Across the Life Span". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 42 (6): 1316–1319. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbw028. PMC 5049521. PMID 27033328.
- ^ Schrimpf LA, Aggarwal A, Lauriello J (June 2018). "Psychosis". Continuum (Minneap Minn). 24 (3): 845–860. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000602. PMID 29851881. S2CID 243933980.
- ^ Bottas A (15 April 2009). "Comorbidity: Schizophrenia With Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder". Psychiatric Times. 26 (4). Archived from the original on 3 April 2013.
- ^ OConghaile A, DeLisi LE (May 2015). "Distinguishing schizophrenia from posttraumatic stress disorder with psychosis". Curr Opin Psychiatry. 28 (3): 249–255. doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000158. PMID 25785709. S2CID 12523516.
- ^ Murray ED, Buttner N, Price BH (2012). "Depression and Psychosis in Neurological Practice". In Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J (eds.). Bradley's neurology in clinical practice. Vol. 1 (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 92–111. ISBN 978-1-4377-0434-1.
- ^ Leucht S, Bauer S, Siafis S, Hamza T, Wu H, Schneider-Thoma J, et al. (November 2021). "Examination of Dosing of Antipsychotic Drugs for Relapse Prevention in Patients With Stable Schizophrenia: A Meta-analysis". JAMA Psychiatry. 78 (11): 1238–1248. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.2130. PMC 8374744. PMID 34406325.
- ^ Cannon TD, Cornblatt B, McGorry P (May 2007). "The empirical status of the ultra high-risk (prodromal) research paradigm". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 33 (3): 661–664. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbm031. PMC 2526144. PMID 17470445.
- ^ Puntis S, Minichino A, De Crescenzo F, Cipriani A, Lennox B, Harrison R (November 2020). "Specialised early intervention teams for recent-onset psychosis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 11 (11): CD013288. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013288.pub2. PMC 8092671. PMID 33135811.
p. 22: There is low-certainty evidence for the use of SEl services in comparison to TAU for a small reduction in psychiatric hospitalisation, and moderate-certainty evidence of a large effect of reduction in disengagement from mental health services. There is moderate-certainty evidence that SEI results in a small reduction of positive (hallucinations, delusions and disordered thinking) and negative symptoms (social withdrawal, flat or blunted affect, and poverty of speech) and low-certainty evidence that it greatly increases satisfaction in care, while there is low-certainty evidence that it improves general functioning and the likelihood of recovery. These effects were only observed during treatment and there was no evidence that outcomes are improved after the treatment has finished, although these were based on only one trial.
- ^ Stafford MR, Jackson H, Mayo-Wilson E, Morrison AP, Kendall T (January 2013). "Early interventions to prevent psychosis: systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ. 346: f185. doi:10.1136/bmj.f185. PMC 3548617. PMID 23335473.
- ^ a b Taylor M, Jauhar S (September 2019). "Are we getting any better at staying better? The long view on relapse and recovery in first episode nonaffective psychosis and schizophrenia". Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology. 9: 204512531987003. doi:10.1177/2045125319870033. PMC 6732843. PMID 31523418.
- ^ Weiden PJ (July 2016). "Beyond Psychopharmacology: Emerging Psychosocial Interventions for Core Symptoms of Schizophrenia". Focus (American Psychiatric Publishing). 14 (3): 315–327. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20160014. PMC 6526802. PMID 31975812.
- ^ McGurk SR, Mueser KT, Feldman K, Wolfe R, Pascaris A (March 2007). "Cognitive training for supported employment: 2–3 year outcomes of a randomized controlled trial". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 164 (3): 437–441. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.164.3.437. PMID 17329468.
- ^ Souaiby L, Gaillard R, Krebs MO (August 2016). "[Duration of untreated psychosis: A state-of-the-art review and critical analysis]". Encephale. 42 (4): 361–366. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2015.09.007. PMID 27161262.
- ^ Fuller Torrey E (June 2015). "Deinstitutionalization and the rise of violence". CNS Spectrums. 20 (3): 207–214. doi:10.1017/S1092852914000753. PMID 25683467. S2CID 22210482.
- ^ a b c "Schizophrenia – Treatment". UK National Health Service. 23 October 2017. Retrieved 8 January 2020.
- ^ Ortiz-Orendain J, Covarrubias-Castillo SA, Vazquez-Alvarez AO, Castiello-de Obeso S, Arias Quiñones GE, Seegers M, et al. (December 2019). "Modafinil for people with schizophrenia or related disorders". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD008661. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008661.pub2. PMC 6906203. PMID 31828767.
- ^ Lally J, MacCabe JH (June 2015). "Antipsychotic medication in schizophrenia: a review". British Medical Bulletin. 114 (1): 169–179. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldv017. PMID 25957394.
- ^ Keks N, Schwartz D, Hope J (October 2019). "Stopping and switching antipsychotic drugs". Australian Prescriber. 42 (5): 152–157. doi:10.18773/austprescr.2019.052. PMC 6787301. PMID 31631928.
- ^ Harrow M, Jobe TH (September 2013). "Does long-term treatment of schizophrenia with antipsychotic medications facilitate recovery?". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 39 (5): 962–5. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbt034. PMC 3756791. PMID 23512950.
- ^ Elkis H, Buckley PF (June 2016). "Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 39 (2): 239–65. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2016.01.006. PMID 27216902.
- ^ Gillespie AL, Samanaite R, Mill J, Egerton A, MacCabe JH (13 January 2017). "Is treatment-resistant schizophrenia categorically distinct from treatment-responsive schizophrenia? a systematic review". BMC Psychiatry. 17 (1): 12. doi:10.1186/s12888-016-1177-y. PMC 5237235. PMID 28086761.
- ^ Essali A, Al-Haj Haasan N, Li C, Rathbone J (January 2009). "Clozapine versus typical neuroleptic medication for schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2009 (1): CD000059. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000059.pub2. PMC 7065592. PMID 19160174.
- ^ Baier M (August 2010). "Insight in schizophrenia: a review". Current Psychiatry Reports. 12 (4): 356–361. doi:10.1007/s11920-010-0125-7. PMID 20526897. S2CID 29323212.
- ^ Peters L, Krogmann A, von Hardenberg L, Bödeker K, Nöhles VB, Correll CU (November 2019). "Long-Acting Injections in Schizophrenia: a 3-Year Update on Randomized Controlled Trials Published January 2016 – March 2019". Current Psychiatry Reports. 21 (12): 124. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1114-0. PMID 31745659. S2CID 208144438.
- ^ Leucht S, Tardy M, Komossa K, Heres S, Kissling W, Salanti G, et al. (June 2012). "Antipsychotic drugs versus placebo for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Lancet. 379 (9831): 2063–2071. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60239-6. PMID 22560607. S2CID 2018124.
- ^ McEvoy JP (2006). "Risks versus benefits of different types of long-acting injectable antipsychotics". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 67 (Suppl 5): 15–18. PMID 16822092.
- ^ a b "FDA Approves Drug with New Mechanism of Action for Treatment of Schizophrenia". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 26 September 2024. Archived from the original on 27 September 2024. Retrieved 27 September 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approves Bristol Myers Squibb's Cobenfy (xanomeline and trospium chloride), a First-In-Class Muscarinic Agonist for the Treatment of Schizophrenia in Adults" (Press release). Bristol Myers Squibb. 27 September 2024. Retrieved 27 September 2024 – via Business Wire.
- ^ Lindenmayer JP, Nasrallah H, Pucci M, James S, Citrome L (1 July 2013). "A systematic review of psychostimulant treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia: Challenges and therapeutic opportunities". Schizophrenia Research. 147 (2): 241–252. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2013.03.019. ISSN 0920-9964.
- ^ Sapienza J, Martini F, Comai S, Cavallaro R, Spangaro M, De Gregorio D, et al. (18 September 2024). "Psychedelics and schizophrenia: a double-edged sword". Molecular Psychiatry: 1–14. doi:10.1038/s41380-024-02743-x. ISSN 1476-5578. PMID 39294303.
- ^ a b Chow CL, Kadouh NK, Bostwick JR, VandenBerg AM (June 2020). "Akathisia and Newer Second-Generation Antipsychotic Drugs: A Review of Current Evidence". Pharmacotherapy. 40 (6): 565–574. doi:10.1002/phar.2404. hdl:2027.42/155998. PMID 32342999. S2CID 216596357.
- ^ Carbon M, Kane JM, Leucht S, Correll CU (October 2018). "Tardive dyskinesia risk with first- and second-generation antipsychotics in comparative randomized controlled trials: a meta-analysis". World Psychiatry. 17 (3): 330–340. doi:10.1002/wps.20579. PMC 6127753. PMID 30192088.
- ^ a b Pharoah F, Mari J, Rathbone J, Wong W (December 2010). Pharoah F (ed.). "Family intervention for schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD000088. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000088.pub2. PMC 4204509. PMID 21154340.
- ^ Bellani M, Ricciardi C, Rossetti MG, Zovetti N, Perlini C, Brambilla P (September 2019). "Cognitive remediation in schizophrenia: the earlier the better?". Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences. 29: e57. doi:10.1017/S2045796019000532. PMC 8061237. PMID 31556864.
- ^ Philipp R, Kriston L, Lanio J, Kühne F, Härter M, Moritz S, et al. (March 2019). "Effectiveness of metacognitive interventions for mental disorders in adults-A systematic review and meta-analysis (METACOG)". Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy. 26 (2): 227–240. doi:10.1002/cpp.2345. PMID 30456821. S2CID 53872643.
- ^ Rouy M, Saliou P, Nalborczyk L, Pereira M, Roux P, Faivre N (July 2021). "Systematic review and meta-analysis of metacognitive abilities in individuals with schizophrenia spectrum disorders" (PDF). Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 126: 329–337. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.03.017. PMID 33757817. S2CID 232288918.
- ^ Dixon LB, Dickerson F, Bellack AS, Bennett M, Dickinson D, Goldberg RW, et al. (January 2010). "The 2009 schizophrenia PORT psychosocial treatment recommendations and summary statements". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 36 (1): 48–70. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbp115. PMC 2800143. PMID 19955389.
- ^ Bond GR, Drake RE (June 2015). "The critical ingredients of assertive community treatment". World Psychiatry. 14 (2): 240–242. doi:10.1002/wps.20234. PMC 4471983. PMID 26043344.
- ^ Smeerdijk M (2017). "[Using resource groups in assertive community treatment; literature review and recommendation]". Tijdschrift voor Psychiatrie. 59 (8): 466–473. PMID 28880347.
- ^ Dieterich M (6 January 2017). "Intensive case management for severe mental illness". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD007906. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007906.pub3. PMC 6472672. PMID 28067944.
- ^ Jauhar S, McKenna PJ, Radua J, Fung E, Salvador R, Laws KR (January 2014). "Cognitive-behavioural therapy for the symptoms of schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis with examination of potential bias". The British Journal of Psychiatry (Review). 204 (1): 20–29. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.112.116285. PMID 24385461.
- ^ a b Jones C, Hacker D, Meaden A, Cormac I, Irving CB, Xia J, et al. (November 2018). "Cognitive behavioural therapy plus standard care versus standard care plus other psychosocial treatments for people with schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 11 (11): CD008712. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008712.pub3. PMC 6516879. PMID 30480760.
- ^ Health Quality Ontario (2018). "Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Psychosis: A Health Technology Assessment". Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 18 (5): 1–141. PMC 6235075. PMID 30443277.
- ^ Ruddy R, Milnes D (October 2005). "Art therapy for schizophrenia or schizophrenia-like illnesses". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD003728. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003728.pub2. PMID 16235338. Archived from the original on 27 October 2011.
- ^ Ruddy RA, Dent-Brown K (January 2007). "Drama therapy for schizophrenia or schizophrenia-like illnesses". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD005378. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005378.pub2. PMID 17253555. Archived from the original on 25 August 2011.
- ^ Galletly C, Castle D, Dark F, et al. (May 2016). "Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists clinical practice guidelines for the management of schizophrenia and related disorders". Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 50 (5): 410–472. doi:10.1177/0004867416641195. PMID 27106681. S2CID 6536743.
- ^ Chien WT, Clifton AV, Zhao S, Lui S (4 April 2019). "Peer support for people with schizophrenia or other serious mental illness". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4 (6): CD010880. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010880.pub2. PMC 6448529. PMID 30946482.
- ^ a b Girdler SJ, Confino JE, Woesner ME (15 February 2019). "Exercise as a Treatment for Schizophrenia: A Review". Psychopharmacology Bulletin. 49 (1): 56–69. PMC 6386427. PMID 30858639.
- ^ a b Firth J (1 May 2017). "Aerobic Exercise Improves Cognitive Functioning in People With Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 43 (3): 546–556. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbw115. PMC 5464163. PMID 27521348.
- ^ Tréhout M, Dollfus S (December 2018). "[Physical activity in patients with schizophrenia: From neurobiology to clinical benefits]". L'Encéphale. 44 (6): 538–547. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2018.05.005. PMID 29983176. S2CID 150334210.
- ^ "Quality statement 7: Promoting healthy eating, physical activity and smoking cessation | Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults". UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. 12 February 2015.
- ^ a b c Firth J, Carney R, Stubbs B, Teasdale SB, Vancampfort D, Ward PB, et al. (October 2018). "Nutritional Deficiencies and Clinical Correlates in First-Episode Psychosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 44 (6): 1275–1292. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbx162. PMC 6192507. PMID 29206972.
- ^ a b c d Rastogi A, Viani-Walsh D, Akbari S, Gall N, Gaughran F, Lally J (October 2020). "Pathogenesis and management of Brugada syndrome in schizophrenia: A scoping review". General Hospital Psychiatry. 67: 83–91. doi:10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2020.09.003. PMC 7537626. PMID 33065406.
- ^ Martone G (April 2018). "Enhancement of recovery from mental illness with l-methylfolate supplementation". Perspectives in Psychiatric Care. 54 (2): 331–334. doi:10.1111/ppc.12227. PMID 28597528.
- ^ a b Firth J, Teasdale SB, Allott K, Siskind D, Marx W, Cotter J, et al. (October 2019). "The efficacy and safety of nutrient supplements in the treatment of mental disorders: a meta-review of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials". World Psychiatry. 18 (3): 308–324. doi:10.1002/wps.20672. PMC 6732706. PMID 31496103.
- ^ Kritharides L, Chow V, Lambert TJ (6 February 2017). "Cardiovascular disease in patients with schizophrenia". The Medical Journal of Australia. 206 (2): 91–95. doi:10.5694/mja16.00650. PMID 28152356. S2CID 5388097.
- ^ Erlangsen A, Eaton WW, Mortensen PB, Conwell Y (February 2012). "Schizophrenia—a predictor of suicide during the second half of life?". Schizophrenia Research. 134 (2–3): 111–117. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2011.09.032. PMC 3266451. PMID 22018943.
- ^ Goroll AH, Mulley AG (2011). Primary Care Medicine: Office Evaluation and Management of The Adult Patient (Sixth ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. Chapter 101. ISBN 978-1-4511-2159-9.
- ^ a b Rizvi S, Gold J, Khan AM (5 August 2019). "Role of Naltrexone in Improving Compulsive Drinking in Psychogenic Polydipsia". Cureus. 11 (8): e5320. doi:10.7759/cureus.5320. PMC 6777931. PMID 31598428.
- ^ Seeman MV (September 2019). "Schizophrenia Mortality: Barriers to Progress". The Psychiatric Quarterly. 90 (3): 553–563. doi:10.1007/s11126-019-09645-0. PMID 31147816. S2CID 170078453.
- ^ Charlson FJ, Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Diminic S, Stockings E, Scott JG, et al. (October 2018). "Global Epidemiology and Burden of Schizophrenia: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 44 (6): 1195–1203. doi:10.1093/schbul/sby058. PMC 6192504. PMID 29762765.
- ^ Smith T, Weston C, Lieberman J (August 2010). "Schizophrenia (maintenance treatment)". American Family Physician. 82 (4): 338–339. PMID 20704164.
- ^ Warner R (July 2009). "Recovery from schizophrenia and the recovery model". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 22 (4): 374–380. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e32832c920b. PMID 19417668. S2CID 26666000.
- ^ Menezes NM, Arenovich T, Zipursky RB (October 2006). "A systematic review of longitudinal outcome studies of first-episode psychosis" (PDF). Psychological Medicine. 36 (10): 1349–62. doi:10.1017/S0033291706007951. PMID 16756689. S2CID 23475454. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 September 2020.
- ^ Coyle JT (2017). "Schizophrenia: Basic and Clinical". Neurodegenerative Diseases. Advances in Neurobiology. Vol. 15. pp. 255–280. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-57193-5_9. ISBN 978-3-319-57191-1. PMID 28674984.
- ^ Isaac M, Chand P, Murthy P (August 2007). "Schizophrenia outcome measures in the wider international community". The British Journal of Psychiatry. Supplement. 50: s71–77. doi:10.1192/bjp.191.50.s71. PMID 18019048.
- ^ Cohen A, Patel V, Thara R, Gureje O (March 2008). "Questioning an axiom: better prognosis for schizophrenia in the developing world?". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 34 (2): 229–244. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbm105. PMC 2632419. PMID 17905787.
- ^ Carlborg A, Winnerbäck K, Jönsson EG, Jokinen J, Nordström P (July 2010). "Suicide in schizophrenia". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 10 (7): 1153–1164. doi:10.1586/ern.10.82. PMID 20586695. S2CID 204385719.
- ^ Tsoi DT, Porwal M, Webster AC (28 February 2013). "Interventions for smoking cessation and reduction in individuals with schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2013 (2): CD007253. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007253.pub3. PMC 6486303. PMID 23450574.
- ^ Sriretnakumar V, Huang E, Müller DJ (2015). "Pharmacogenetics of clozapine treatment response and side-effects in schizophrenia: an update". Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 11 (11): 1709–1731. doi:10.1517/17425255.2015.1075003. PMID 26364648. S2CID 207492339.
- ^ de Leon J, Diaz FJ (July 2005). "A meta-analysis of worldwide studies demonstrates an association between schizophrenia and tobacco smoking behaviors". Schizophrenia Research. 76 (2–3): 135–157. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2005.02.010. PMID 15949648. S2CID 32975940.
- ^ a b Keltner NL, Grant JS (November 2006). "Smoke, smoke, smoke that cigarette". Perspectives in Psychiatric Care. 42 (4): 256–261. doi:10.1111/j.1744-6163.2006.00085.x. PMID 17107571.
- ^ Kumari V, Postma P (January 2005). "Nicotine use in schizophrenia: the self medication hypotheses". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 29 (6): 1021–1034. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.02.006. PMID 15964073. S2CID 15581894.
- ^ Cai L, Huang J (2018). "Schizophrenia and risk of dementia: a meta-analysis study". Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 14: 2047–2055. doi:10.2147/NDT.S172933. PMC 6095111. PMID 30147318.
- ^ Ng R, Fish S, Granholm E (30 January 2015). "Insight and theory of mind in schizophrenia". Psychiatry Research. 225 (1–2): 169–174. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2014.11.010. PMC 4269286. PMID 25467703.
- ^ Bora E (December 2017). "Relationship between insight and theory of mind in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis". Schizophrenia Research. 190: 11–17. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2017.03.029. PMID 28302393. S2CID 36263370.
- ^ Darmedru C, Demily C, Franck N (April 2018). "[Preventing violence in schizophrenia with cognitive remediation]". L'Encephale. 44 (2): 158–167. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2017.05.001. PMID 28641817.
- ^ Richard-Devantoy S, Bouyer-Richard AI, Jollant F, Mondoloni A, Voyer M, Senon JL (August 2013). "[Homicide, schizophrenia and substance abuse: a complex interaction]". Revue d'Épidemiologie et de Santé Publique. 61 (4): 339–350. doi:10.1016/j.respe.2013.01.096. PMID 23816066.
- ^ Sedgwick O, Young S, Baumeister D, Greer B, Das M, Kumari V (December 2017). "Neuropsychology and emotion processing in violent individuals with antisocial personality disorder or schizophrenia: The same or different? A systematic review and meta-analysis". The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 51 (12): 1178–1197. doi:10.1177/0004867417731525. PMID 28992741. S2CID 206401875.
- ^ Charlson F, van Ommeren M, Flaxman A, Cornett J, Whiteford H, Saxena S (July 2019). "New WHO prevalence estimates of mental disorders in conflict settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Lancet. 394 (10194): 240–248. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30934-1. PMC 6657025. PMID 31200992.
- ^ Kirkbride JB, Fearon P, Morgan C, Dazzan P, Morgan K, Tarrant J, et al. (March 2006). "Heterogeneity in incidence rates of schizophrenia and other psychotic syndromes: findings from the 3-center AeSOP study". Archives of General Psychiatry. 63 (3): 250–258. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.3.250. PMID 16520429.
- ^ Kirkbride JB, Fearon P, Morgan C, Dazzan P, Morgan K, Murray RM, et al. (June 2007). "Neighbourhood variation in the incidence of psychotic disorders in Southeast London". Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology. 42 (6): 438–445. doi:10.1007/s00127-007-0193-0. PMID 17473901. S2CID 19655724.
- ^ [needs update] Ayuso-Mateos JL (15 August 2006). "Global burden of schizophrenia in the year 2000" (PDF). World Health Organization. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 27 February 2013.
- ^ Heinrichs RW (2003). "Historical origins of schizophrenia: two early madmen and their illness". Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences. 39 (4): 349–363. doi:10.1002/jhbs.10152. PMID 14601041.
- ^ a b Kuhn R, Cahn CH (September 2004). "Eugen Bleuler's concepts of psychopathology". History of Psychiatry. 15 (59 Pt 3): 361–366. doi:10.1177/0957154X04044603. PMID 15386868. S2CID 5317716.
- ^ "Schizophrenia | Definition of Schizophrenia by Lexico". Lexico Dictionaries | English. Archived from the original on 10 March 2020.
- ^ [page needed] Schneider K (1959). Clinical Psychopathology (5th ed.). New York: Grune & Stratton.
- ^ [page needed] Moore D (25 April 2008). Textbook of Clinical Neuropsychiatry (Second ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 9781444109740.
- ^ Tandon R, Gaebel W, Barch DM, Bustillo J, Gur RE, Heckers S, et al. (October 2013). "Definition and description of schizophrenia in the DSM-5". Schizophrenia Research. 150 (1): 3–10. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2013.05.028. PMID 23800613. S2CID 17314600.
- ^ Picardi A (2019). "The Two Faces of First-Rank Symptoms". Psychopathology. 52 (4): 221–231. doi:10.1159/000503152. PMID 31610542. S2CID 204702486.
- ^ Reed GM, First MB, Kogan CS, Hyman SE, Gureje O, Gaebel W, et al. (February 2019). "Innovations and changes in the ICD-11 classification of mental, behavioural and neurodevelopmental disorders". World Psychiatry. 18 (1): 3–19. doi:10.1002/wps.20611. PMC 6313247. PMID 30600616.
- ^ "Updates to DSM-5 Criteria & Text". www.psychiatry.org. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ Tandon R (July 2014). "Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders in Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-5: Clinical Implications of Revisions from DSM-IV". Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine. 36 (3): 223–225. doi:10.4103/0253-7176.135365. PMC 4100404. PMID 25035542.
- ^ a b Lane C (5 May 2010). "How Schizophrenia Became a Black Disease: An Interview With Jonathan Metzl". Psychology Today. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ^ [page needed] Metz J (2010). The Protest Psychosis. Beacon Press. ISBN 978-0-8070-8592-9.
- ^ Wilson M (March 1993). "DSM-III and the transformation of American psychiatry: a history". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 150 (3): 399–410. doi:10.1176/ajp.150.3.399. PMID 8434655.
- ^ Fischer BA (December 2012). "A review of American psychiatry through its diagnoses: the history and development of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders". The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. 200 (12): 1022–1030. doi:10.1097/NMD.0b013e318275cf19. PMID 23197117. S2CID 41939669.
- ^ a b Jones K (March 2000). "Insulin coma therapy in schizophrenia". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 93 (3): 147–149. doi:10.1177/014107680009300313. PMC 1297956. PMID 10741319.
- ^ Jobes DA, Chalker SA (26 September 2019). "One Size Does Not Fit All: A Comprehensive Clinical Approach to Reducing Suicidal Ideation, Attempts, and Deaths". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 16 (19): 3606. doi:10.3390/ijerph16193606. PMC 6801408. PMID 31561488.
- ^ Ali SA, Mathur N, Malhotra AK, Braga RJ (April 2019). "Electroconvulsive Therapy and Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review". Molecular Neuropsychiatry. 5 (2): 75–83. doi:10.1159/000497376. PMC 6528094. PMID 31192220.
- ^ Mashour GA, Walker EE, Martuza RL (June 2005). "Psychosurgery: past, present, and future". Brain Research. Brain Research Reviews. 48 (3): 409–419. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.09.002. PMID 15914249. S2CID 10303872.
- ^ Mendez J (1 February 2013). "Report of the Special Rapporteur on torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment" (PDF). Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights. Retrieved 22 August 2022.
- ^ Turner T (January 2007). "Chlorpromazine: unlocking psychosis". BMJ. 334 Suppl 1 (suppl): s7. doi:10.1136/bmj.39034.609074.94. PMID 17204765. S2CID 33739419.
- ^ Aringhieri S (December 2018). "Molecular targets of atypical antipsychotics: From mechanism of action to clinical differences". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 192: 20–41. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.06.012. PMID 29953902. S2CID 49602956.
- ^ Park YS, Sang M, Jun JY, Kim SJ (2014). "Psychiatry in former socialist countries: implications for north korean psychiatry". Psychiatry Investigation. 11 (4): 363–370. doi:10.4306/pi.2014.11.4.363. ISSN 1738-3684. PMC 4225199. PMID 25395966.
- ^ [page needed] Gosden R (2001). Punishing the patient: how psychiatrists misunderstand and mistreat schizophrenia. Melbourne: Scribe Publications. ISBN 0-908011-52-0. OCLC 47177633.
- ^ Sfera A (September 2013). "Can Psychiatry be Misused Again?". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 4: 101. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00101. PMC 3766833. PMID 24058348.
- ^ Merskey H (15 October 1988). "IPPNW: Forum for Soviet anti-American propaganda?". CMAJ: Canadian Medical Association Journal. 139 (8): 699–700. ISSN 0820-3946. PMC 1268271.
- ^ Wu EQ, Birnbaum HG, Shi L, Ball DE, Kessler RC, Moulis M, et al. (September 2005). "The economic burden of schizophrenia in the United States in 2002". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 66 (9): 1122–1129. doi:10.4088/jcp.v66n0906. PMID 16187769.
- ^ McEvoy JP (2007). "The costs of schizophrenia". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 68 (Suppl 14): 4–7. PMID 18284271.
- ^ Zhang W, Amos TB, Gutkin SW, et al. (2018). "A systematic literature review of the clinical and health economic burden of schizophrenia in privately insured patients in the United States". Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 10: 309–320. doi:10.2147/CEOR.S156308. PMC 5997131. PMID 29922078.
- ^ Yamaguchi S, Mizuno M, Ojio Y, Sawada U, Matsunaga A, Ando S, et al. (June 2017). "Associations between renaming schizophrenia and stigma-related outcomes: A systematic review". Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 71 (6): 347–362. doi:10.1111/pcn.12510. PMID 28177184.
- ^ Sato M (February 2006). "Renaming schizophrenia: a Japanese perspective". World Psychiatry. 5 (1): 53–55. PMC 1472254. PMID 16757998.
- ^ Park SC, Park YC (January 2020). "Korea in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition". Journal of Korean Medical Science. 35 (2) (Fifth ed.): e6. doi:10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e6. PMC 6955430. PMID 31920014.
- ^ Fazel S, Gulati G, Linsell L, Geddes JR, Grann M (August 2009). "Schizophrenia and violence: systematic review and meta-analysis". PLOS Medicine. 6 (8): e1000120. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000120. PMC 2718581. PMID 19668362.
- ^ Owen PR (July 2012). "Portrayals of schizophrenia by entertainment media: a content analysis of contemporary movies". Psychiatr Serv. 63 (7): 655–9. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201100371. PMID 22555313.
- ^ Katschnig H (October 2018). "Psychiatry's contribution to the public stereotype of schizophrenia: Historical considerations". J Eval Clin Pract. 24 (5): 1093–1100. doi:10.1111/jep.13011. PMC 6174929. PMID 30112785.
- ^ Chen M, Lawrie S (December 2017). "Newspaper depictions of mental and physical health". BJPsych Bulletin. 41 (6): 308–313. doi:10.1192/pb.bp.116.054775. PMC 5709678. PMID 29234506.
- ^ Dyga K, Stupak R (28 February 2018). "Ways of understanding of religious delusions associated with a change of identity on the example of identification with Jesus Christ". Psychiatria Polska. 52 (1): 69–80. doi:10.12740/PP/64378. PMID 29704415.
- ^ Dein S, Littlewood R (July 2011). "Religion and psychosis: a common evolutionary trajectory?". Transcultural Psychiatry. 48 (3): 318–335. doi:10.1177/1363461511402723. PMID 21742955. S2CID 12991391.
- ^ Dougall N, Maayan N, Soares-Weiser K, McDermott LM, McIntosh A (20 August 2015). "Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (8): CD006081. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006081.pub2. hdl:1893/22520. PMC 9395125. PMID 26289586.
- ^ a b Nathou C, Etard O, Dollfus S (2019). "Auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia: current perspectives in brain stimulation treatments". Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 15: 2105–2117. doi:10.2147/NDT.S168801. PMC 6662171. PMID 31413576.
- ^ Kraguljac NV, McDonald WM, Widge AS, Rodriguez CI, Tohen M, Nemeroff CB (January 2021). "Neuroimaging Biomarkers in Schizophrenia". Am J Psychiatry. 178 (6): 509–521. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20030340. PMC 8222104. PMID 33397140.
- ^ Khavari B, Cairns MJ (August 2020). "Epigenomic Dysregulation in Schizophrenia: In Search of Disease Etiology and Biomarkers". Cells. 9 (8): 1837. doi:10.3390/cells9081837. PMC 7463953. PMID 32764320.
- ^ Goldsmith DR, Crooks CL, Walker EF, Cotes RO (April 2018). "An Update on Promising Biomarkers in Schizophrenia". Focus (American Psychiatric Publishing). 16 (2): 153–163. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20170046. PMC 6526854. PMID 31975910.
- ^ Kumar S, Reddy PH (September 2016). "Are circulating microRNAs peripheral biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease?". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862 (9): 1617–1627. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.06.001. PMC 5343750. PMID 27264337.
- ^ van den Berg MM, Krauskopf J, Ramaekers JG, et al. (February 2020). "Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders". Prog Neurobiol. 185: 101732. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2019.101732. PMID 31816349. S2CID 208790466.
- ^ Palaniyappan L, Liddle PF (24 April 2013). "Diagnostic Discontinuity in Psychosis: A Combined Study of Cortical Gyrification and Functional Connectivity". Schizophrenia Bulletin. 40 (3): 675–684. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbt050. ISSN 1745-1701. PMC 3984507. PMID 23615812.
External links

